Figure 5.
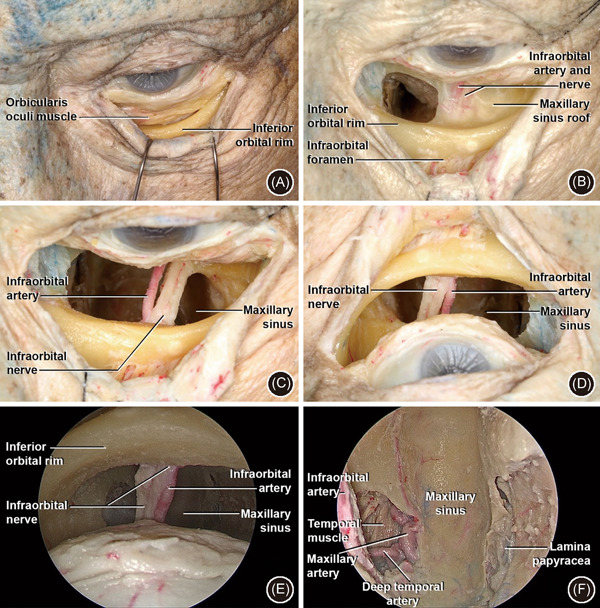
Transconjunctival approach. (A) Left side: conjunctival incision just below to lower border of the tarsus with detachment between septum and orbicularis oculi muscle in the orbital rim; (B) subperiosteal detachment of orbital floor and identification of ION and IOA. The IOF with ION and IOA are identified in the anterior surface of the inferior orbital rim. A window has been opened in the orbit floor medial to the ION; (C) the bone has been drilled medial and lateral to the ION and IOA—anatomic view; (D) surgical view; of C (E): 0‐degree endoscopic superior view of MS, with ION and IOA—surgical view; (F): 0 degree endoscopic superior view of MS, with IMAX and DTA laterally (on the left) and papyracea lamina medially (on the right)—surgical view. DTA, deep temporal artery; IMAX, internal maxillary artery; IOA, infraorbital artery; IOF, infraorbital foramen; ION, infraorbital nerve; MS, maxillary sinus
