Figure 9.
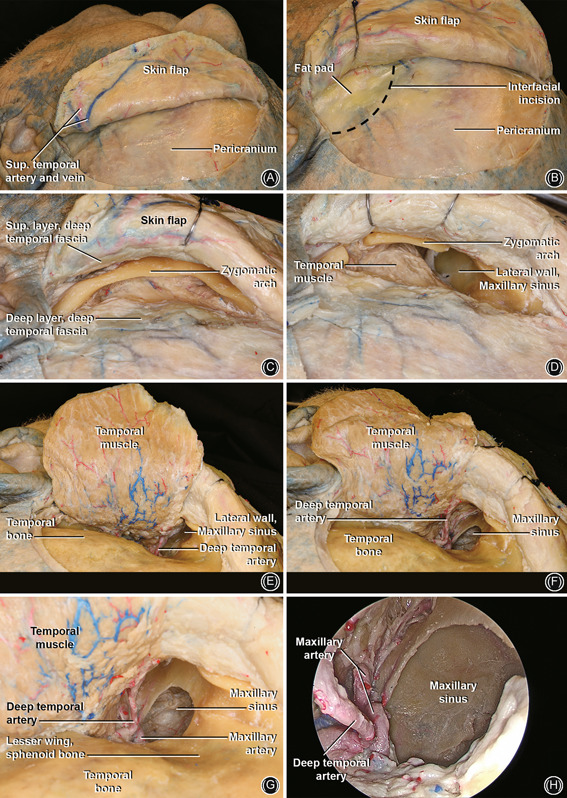
Preauricular hemicoronal approach. (A) Left side: incision 1–2 cm posterior to the hairline extending from the preauricular area towards the forehead midline. (B) Raise the skin flap above the periosteal layer. An incision is performed at the level of the fat pad (black dashed line) 3–4 cm above supraorbital ridge, and dissection is carried out anteriorly in an interfascial plane to expose the zygoma. The superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia is kept with the skin flap to protect the frontal branches of the facial nerve that runs superficial to the superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia. (C) Overview of the zygoma and the superficial layer of the deep temporal fascia superiorly; (D) osteotomies in the lateral and medial portion of the zygomatic arch; (E) elevation of the temporal muscle flap and visualization of posterior/lateral wall of MS. Note the DTA; (F) open window in the lateral wall of MS. (G) Enlarged view of (F), note the DTA and IMAX; (H) 0 degree endoscopic lateral view of MS. DTA, deep temporal artery; IMAX, internal maxillary artery; MS, maxillary sinus
