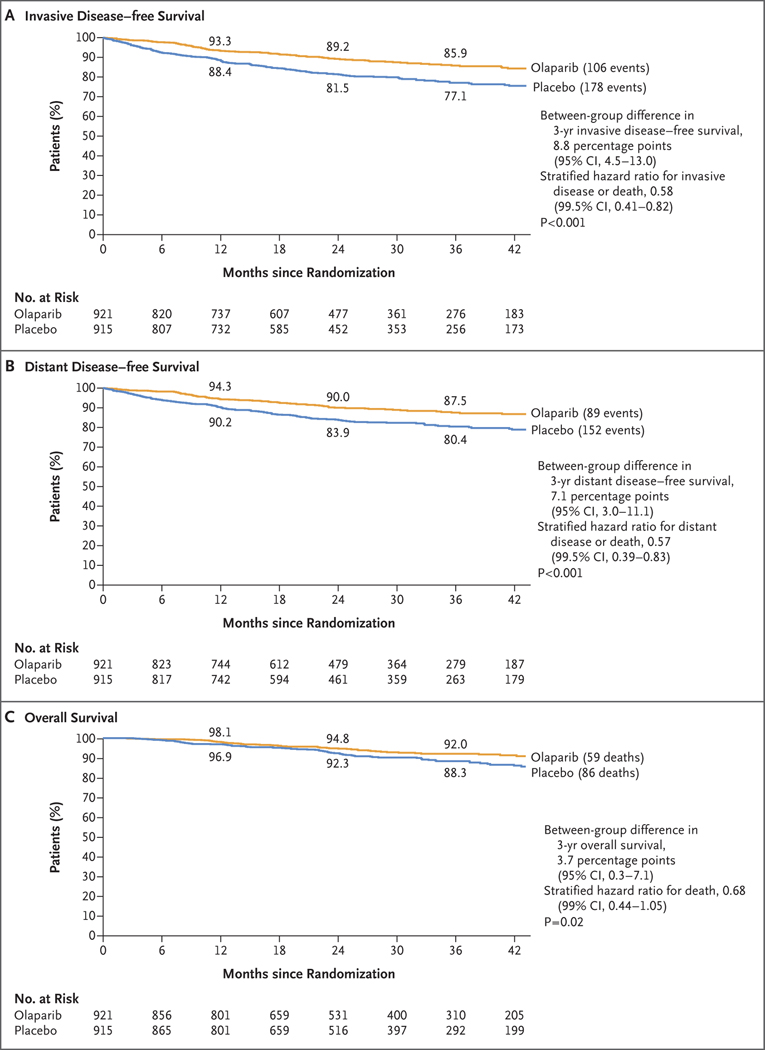
Figure 1. Kaplan–Meier Estimates of Survival.
In accordance with the standardized definitions for efficacy end points (STEEP) system, the primary end point of invasive disease–free survival (Panel A) was defined as the time from randomization until the date of one of the following events: ipsilateral invasive breast tumor, locoregional invasive disease, distant recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, second primary invasive cancer, or death from any cause. Data for patients without a documented event of invasive disease or death were censored at the date they were last known to be disease-free. Distant disease–free survival (Panel B) was defined as the time from randomization until documented evidence of first distant recurrence of breast cancer or death. Distant recurrence includes the following events: distant recurrence (metastatic breast cancer that has either been biopsy confirmed or radiologically diagnosed as recurrent invasive breast cancer); death attributable to any cause, including breast cancer, nonbreast cancer, or unknown cause; and second primary nonbreast invasive cancer. Evidence of distant recurrence requires either radiologic examination or histopathological confirmation by biopsy. Overall survival (Panel C) was defined as the time from the date of randomization until death due to any cause; the P value for the boundary for significance in this prespecified event-driven interim analysis was less than 0.01. For invasive disease–free survival and distant disease–free survival, 99.5% confidence intervals are shown for the hazard ratios because a P value of less than 0.005 is required to indicate statistical significance for these end points. Similarly, the 99% confidence interval is shown for the hazard ratio for overall survival because a P value of less than 0.01 is required to indicate statistical significance for overall survival. On the basis of the pooling strategy for stratification factors described in Section 3.4 in the Supplementary Appendix, both the Cox model hazard-ratio estimation and the log-rank test were performed with hormone-receptor status as the single stratification factor. The event-free rates at 12, 24, and 36 months in each group are displayed above and below the curves.