FIGURE 2.
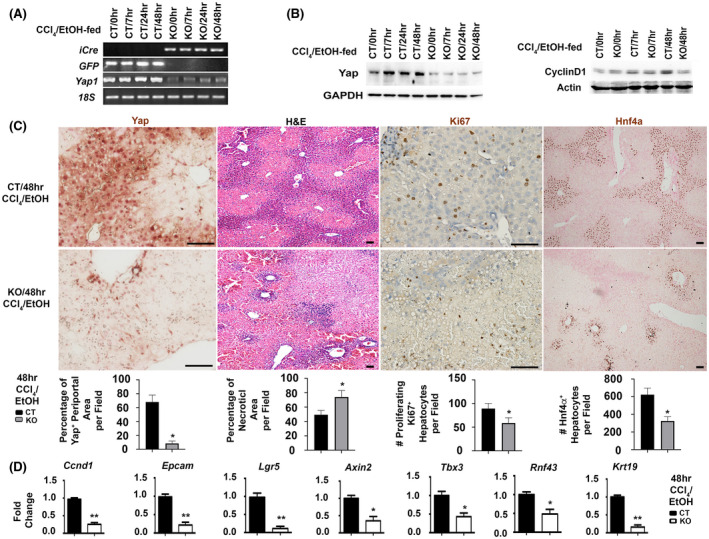
Yap1 deletion inhibits hepatocyte proliferation and downregulates progenitor related genes after ethanol/CCl4 treatment. Control (CT) animals or hepatocyte‐specific knockouts (KO) were generated by tail vein injection of AAV8‐GFP or AAV8‐iCre on floxed homozygotes followed by ethanol‐feeding and a single dose of CCl4 intoxication (n = 5/per group per time point). Yap1 deletion in hepatocytes was confirmed in RT‐PCR analysis (A), Western blotting (B), and IHC (C). Yap loss in periportal hepatocytes of KO livers at 48 h after ethanol/CCl4‐induced injury was associated with massive hepatic necrosis shown in H&E staining, reduced proliferating hepatocytes in Ki67 staining, and decreased number of Hnf4a+ periportal cells. Scale bar: 100 μm. Values were means ± SEM based on quantification of images from more than 10 fields per mouse (n = 5 mice per group). (D) Q‐RT‐PCR analysis detected downregulation of Ccnd1 and progenitor related transcripts in the ethanol‐fed Yap1 KO livers at 48 h post CCl4 intoxication. Values represent means ± SD in relation to controls from three independent experiments. *p < .05, **p < .01
