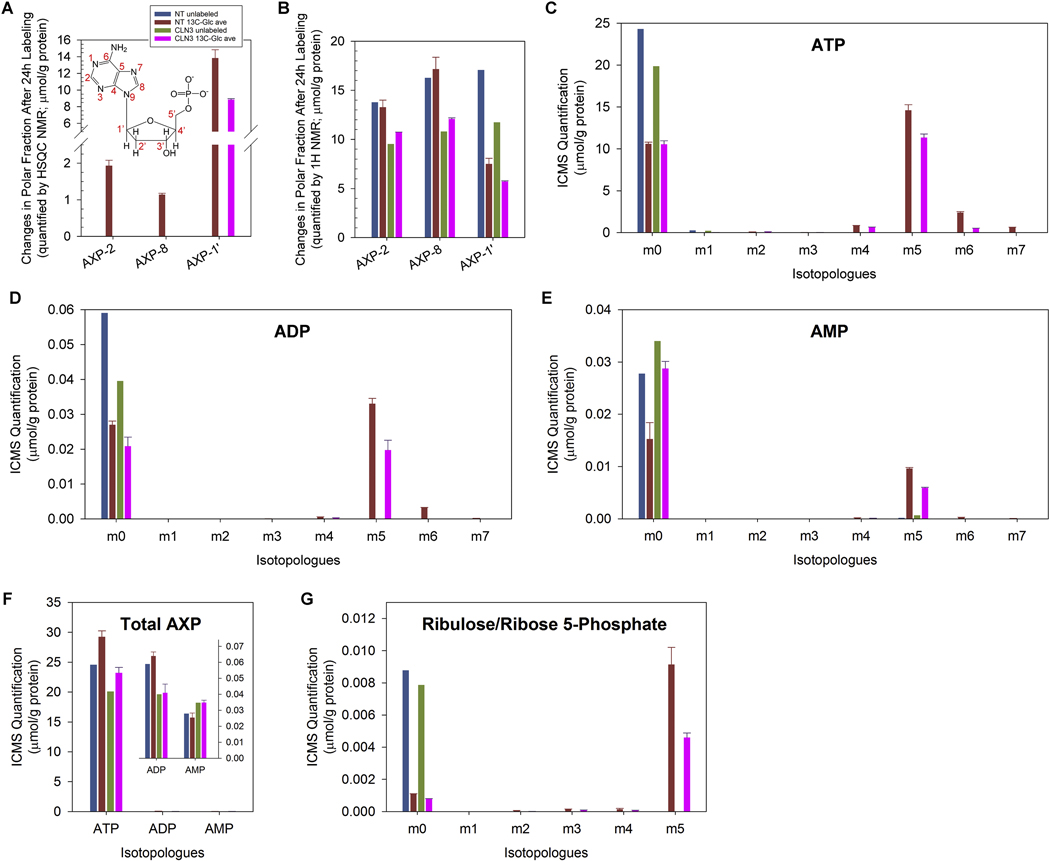
Figure 7. Loss of CLN3 led to decreased intracellular ATP levels.
(A) 1H{13C}-HSQC NMR spectra of polar extracts of the cells at 24 h after 13C6-glucose labeling showed that CLN3-deficient RPE-1 cells had depleted intracellular levels of 13C-labeled AXP (i.e., AMP, ADP and/or ATP) with labeling at position 2, 8 and 1’. The inset shows the atom positions of AMP. (B) 1H NMR spectra of polar extracts of the cells at 24 h after 13C6-glucose labeling showed that CLN3-deficient RPE-1 cells had reduced intracellular levels of unlabeled AXP when detected at positions 2, 8 and 1’. (C-E) ICMS analyses of RPE-1 cell polar extracts showed that CLN3 deficiency led to reduced intracellular (C) 13C5-ATP, (D) 13C5-ADP and (E) 13C5-AMP. (F) ICMS analyses of RPE-1 cell polar extracts showed that CLN3 deficiency led to reduced intracellular total ATP and ADP levels but increased intracellular total AMP levels. (G) ICMS analyses of RPE-1 cell polar extracts showed that CLN3 deficiency led to reduced intracellular 13C5-ribulose-5-phosphate and/or 13C5-ribose-5-phosphate. m1-m7 indicate singly, doubly, triply, quadruply, quintuply, sextuply, and septuplet 13C-labeled isotopologues, respectively. Metabolite amounts were normalized by protein amounts of corresponding samples. Owing to limited resources, the SIRM experiment only included single unlabeled sample and duplicated labeled samples for either non-targeting or CLN3 exon-8 siRNA treatment. For all SIRM quantification results (A-G), means and standard errors were plotted for labeled samples.