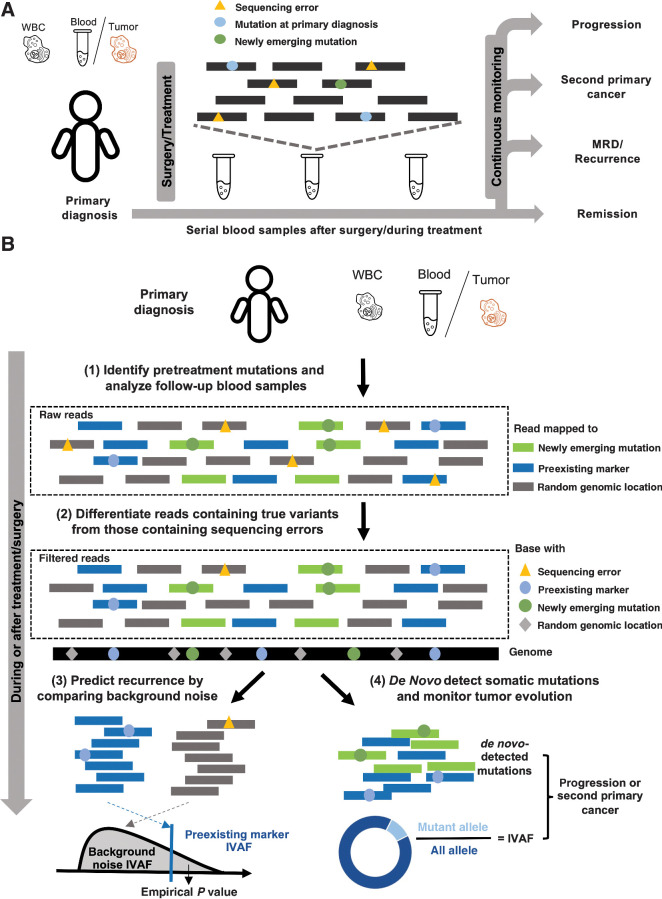
Figure 1.
Cancer monitoring in plasma samples by tracking preexisting tumor mutations and newly emerging tumor mutations. A, Illustration of the sample collection for cfDNA-based cancer monitoring. Prior to surgery or therapy, a plasma or tumor sample and a WBC sample are collected to generate the preexisting tumor profile. Serial blood samples are collected to detect MRD/recurrence and monitor tumor evolution after treatment. B, Illustration of the method workflow. In the pretreatment samples, clonal tumor mutations are identified for tumor tracking in the posttreatment samples. Given a posttreatment plasma sample, the tumor fraction is calculated from the preexisting clonal tumor mutations and compared with a sample-specific background distribution. The empirical P value of the tumor fraction is used to predict MRD/recurrence. Furthermore, de novo somatic mutations are detected using cfSNV between the posttreatment plasma and WBC samples. A second primary cancer is predicted by a logistic regression model that accounts for both the amount of de novo mutations and the corresponding tumor fraction.