Figure 8.
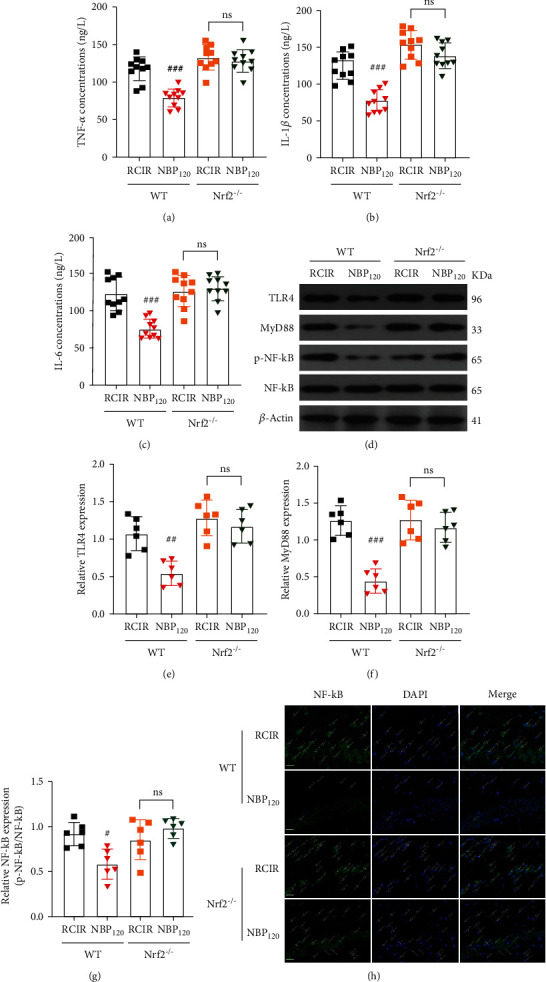
NBP alleviated RCIR-induced inflammatory response, but with reduced inhibitory role in Nrf2−/− mice. (a)–(c) ELISA analysis showing the expression of the inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the hippocampus of WT and Nrf2−/− mice 4 weeks after RCIR. n = 10 per group. (d)–(g) Western blot analysis showing the expression of TLR4, MyD88, and p-NF-κB in WT and Nrf2−/− mice at 4 weeks after RCIR. n = 6 per group. β-Actin was used as an internal control. (h) Representative immunofluorescent micrographs of the hippocampus after staining with NF-κB primary antibody in WT and Nrf2−/− mice 4 weeks after RCIR injury. Green fluorescence, NF-κB-positive cells; white arrow, nuclear translocation of NF-κB after RCIR with or without NBP treatment. Scale bar = 20 μm. n = 3 in each group. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, the WT + NBP120 vs. the WT + RCIR group; ns: not significant, as indicated. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.
