Fig. 1. Generation of pyroglutamated (pE) peptides involved in Alzheimer’s disease.
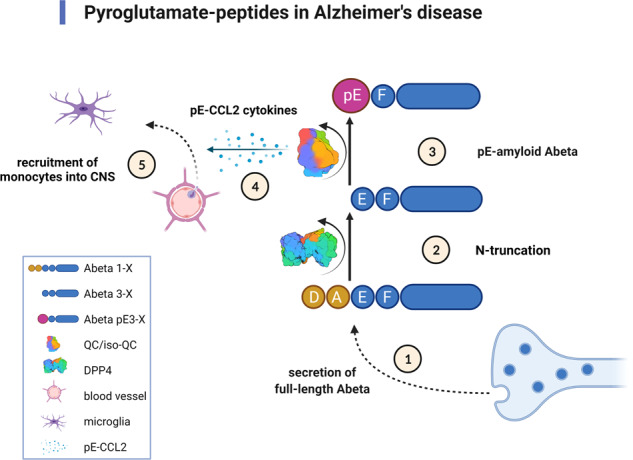
① The N-terminus of full-length Aβ is generated by BACE1 or meprin-β and secreted by neurons. ② Next, N-terminal amino acids are cleaved off by aminopeptidase A (APA), meprin-β or dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4). ③ Glutamate at position three of the N-terminus of Aβ is subsequently post-translationally modified into N-terminal pyroglutamate (pE) by dehydration catalyzed by glutaminyl cyclase (QC) activity. ④ The isoenzyme of QC, isoQC, predominantly converts the N-terminus of chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) into pE-CCL2 ⑤ triggering monocyte recruitment into the central nervous system (CNS). The surface structure of DPP4 [84] and of QC [85] was taken from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). Created with BioRender.com.
