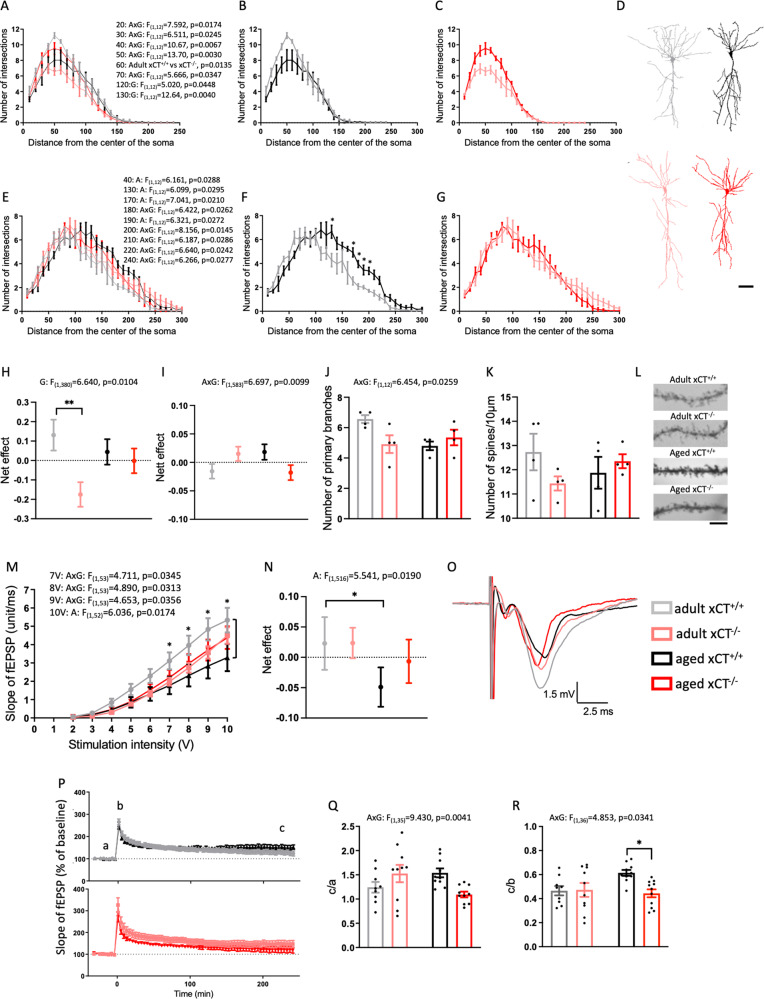
Fig. 4. xCT deletion affects the age-related changes in dendritic arborization and protects against age-related impairment in hippocampal neurotransmission.
Dendritic arborization of the basal (A–C, H) and apical tree (E–G, I) of CA1 pyramidal neurons was evaluated using a Sholl analysis (n = 4 mice/group; 17–18 neurons/group; representative tracings, D). The net effect represents the average of each group, corrected for the co-variate ‘distance from the center of the soma’ and relative to the average response of all groups (H, I). The number of primary branches was counted (J) and on each neuron spine density was calculated on 3–4 segments (total of 63–77 segments/group; K). Representative pictures of the dendritic spines (L). To generate input/output (I/O) curves, the mean of 2 electrodes/slice and 1–2 slices/animal was used (M; 13 slices from 7 adult xCT+/+ mice, 17 slices from 9 adult xCT−/− mice, 11 slices from 6 aged xCT+/+ mice, 16 slices from 9 aged xCT−/− mice). The net effect represents the average response of each group, corrected for the co-variate ‘stimulation intensity’ and relative to the average response of all groups (N). Representative tracings of fEPSP (stimulation of 8 V, O). LTP measurements in 9 slices from 7 adult xCT+/+ mice, 10 slices from 8 adult xCT−/− mice, 10 slices from 6 aged xCT+/+ mice, 11 slices from 8 aged xCT−/− mice (P–R). The ratio of the normalized fEPSP slope 4 h after the high-frequency stimulation over the slope before (Q) and immediately after (R) the stimulation, was used to quantify LTP. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. To calculate the net effect for the Scholl analysis and I/O curves, a longitudinal analysis was performed using a backward selected model and a correction for the respective co-variates, with an autoregressive model followed by a two-way ANOVA and a one-sided Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (H, I, N, see Supplementary Methods). All other data are analyzed using a two-way ANOVA or a Kruskal–Wallis test in case of non-normal distributed data (A–C, distance 60, 160, and 170) (see Supplementary Table 4): A aging effect, G genotype effect, AxG interaction effect; Sidak’s multiple comparisons; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Scale bar: 50 μm (D), 5 μm (L).