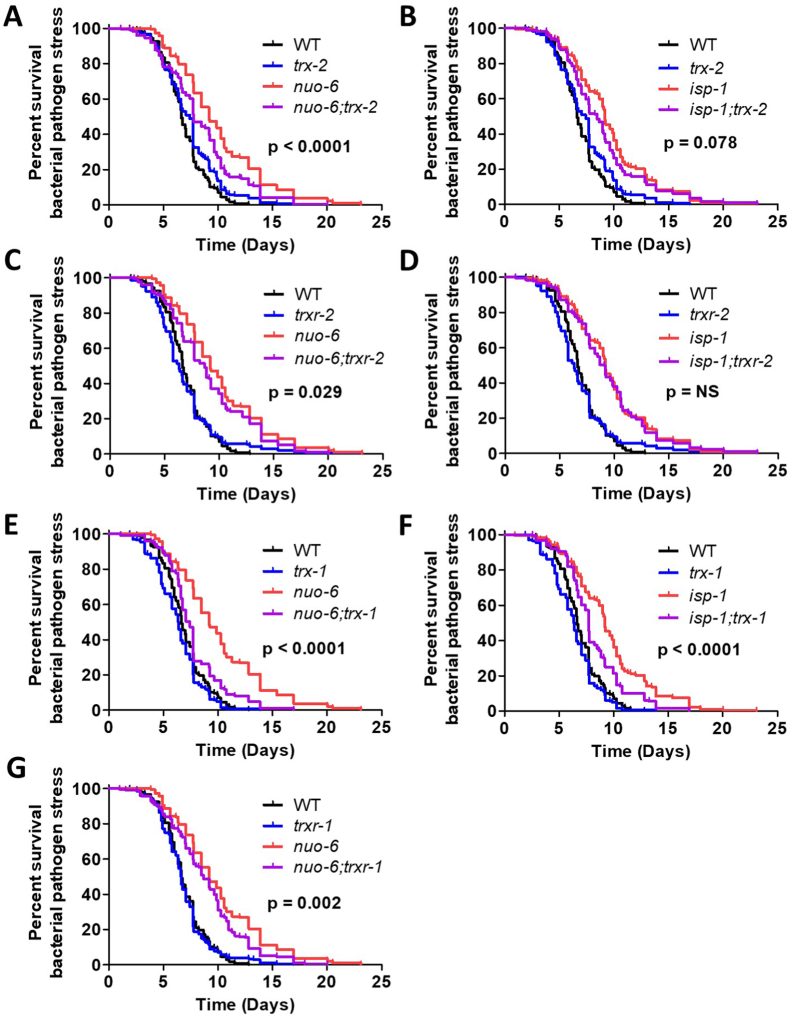
Fig. 8.
Disruption of mitochondrial thioredoxin system increases sensitivity to bacterial pathogens in long-lived mitochondrial mutants. Survival of bacterial pathogen stress was assessed by exposing worms to P. aeruginosa strain PA14. Disruption of trx-2 significantly reduced the ability of nuo-6 worms to survive bacterial pathogen stress (A), while isp-1;trx-2 worms only exhibited a trend towards decreased survival compared to isp-1 mutants (B). Similarly, loss of trxr-2 reduced bacterial pathogen resistance in nuo-6 worms (C), but not isp-1 worms (D). Deletion of trx-1 decreased the survival of wild-type, nuo-6 (E) and isp-1 (F) worms exposed to P. aeruginosa. Disruption of trxr-1 significantly reduced bacterial pathogen resistance in nuo-6 worms (G). Statistical significance was assessed using a log-rank test. p-values indicate significance of difference between red and purple lines. Six biological replicates were performed. Raw data for this figure can be found in Table S1. A bar graph of this data can be found in Fig. S5. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)