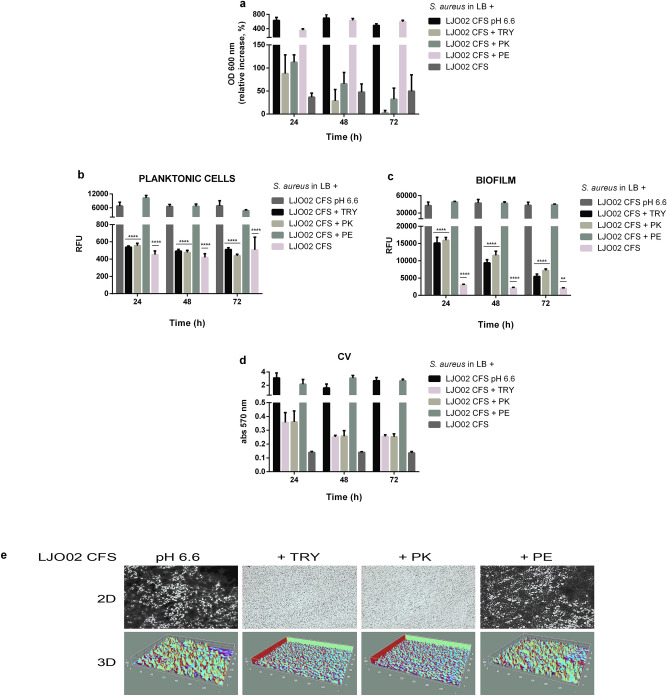
Figure 4.
Evaluation of the effect of modified CFSs from LJO02 produced in TIL on S. aureus growth and biofilm formation. (a) S. aureus planktonic cell and biofilm OD600 after 24, 48, and 72 h of incubation with the CFSs from LJO02 in TIL at pH 6.6 or enzymatically-digested (considering T0 = 100% viability in each experimental condition). OD = optical density. CFS = cell-free supernatant. TRY = trypsin; PK = proteinase K; PE = pepsin. (b) Planktonic cell and (c) biofilm S. aureus viability assessment after 24, 48, and 72 h of incubation with modified CFSs. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments (n = 4). Trypsin and proteinase K-treated CFSs significantly reduce the planktonic cell viability compared to basification and pepsin treatment, similarly to what occurs with the untreated CFS (p < 0.0001). Biofilm viability is significantly reduced by trypsin and proteinase K-treated CFSs with respect to basification and pepsin at all tested times (p < 0.0001), but undigested CFS still shows the best performance (p < 0.0001 at 24 and 48 h, and p < 0.01 at 72 h with respect to trypsin and proteinase K-digested CFS). Two-way ANOVA was applied with Tukey’s comparison test. **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. RFU = relative fluorescence units. (d) CV-reading at 570 nm of S. aureus biofilm at the 3 tested time points. (e) Representative 2D and 3D images of CV-stained S. aureus biofilm after 72 h of treatment with the modified CFSs. 2D pictures magnification: 460 X. Scale bar: 100 μm.