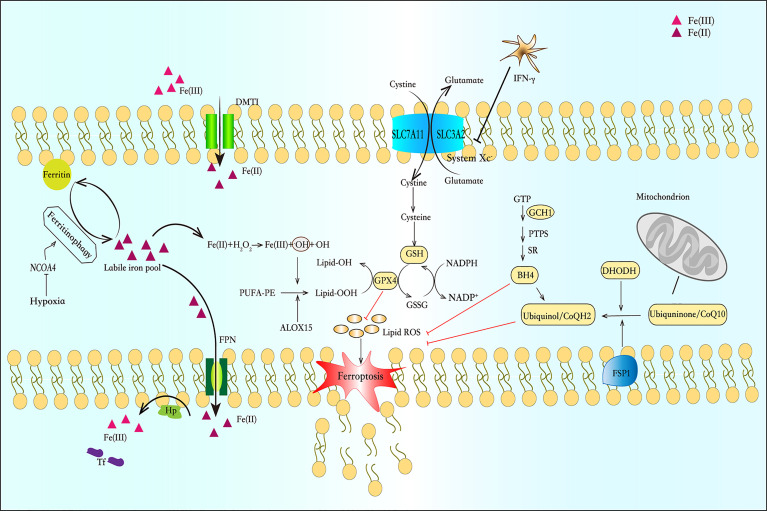
Figure 1.
Iron metabolism and the pathway of ferroptosis. Ferrireductase (DMT1) converts Fe (III) to Fe (II). Some of Fe (II) is bound to ferritin and forms cytosolic labile iron pool (cLIP), and some crosses the basolateral membrane through ferroportin (FPN) into the plasma to combine with transferrin (TF). Fe (II) can initiate liposome peroxidation through the Fenton reaction. The system is a counter-transport that can ingest cystine and excrete glutamic acid to synthesize glutathione (GSH). Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is a selenium enzyme that catalyzes GSH into oxidized glutathione (GSSG) and reduces toxic peroxides to non-toxic hydroxyl compounds. And the FSP1-CoQ-NADPH pathway and DHODH can inhibit lipid peroxidation and protect cells from ferroptosis by generating ubiquinol. In the GCH-BH4 pathway, GCH1 resists ferroptosis through its metabolite BH4. BH4 acts as a free-radical-trapping antioxidant or participates in ubiquinone synthesis to inhibit lipid peroxidation.