Fig. 5. Binding of charge-reduced NV9 variants.
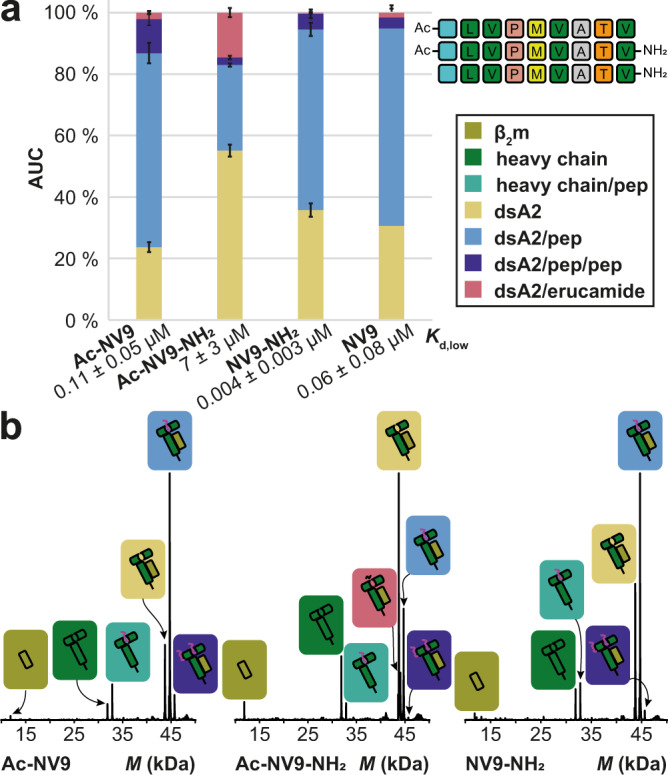
a The AUC is determined over the entire spectrum for the respective mass species, which is depicted along with error bars that represent the corresponding standard deviation. “dsA2” corresponds to the empty complex, “dsA2/pep” to dsA2 bound to one peptide, “dsA2/pep/pep” to dsA2 bound to two molecules of this certain peptide and “dsA2/erucamide” to dsA2 bound to erucamide respectively. By modifying only one terminus (Ac-NV9 and NV9-NH2), the affinity of the peptide to dsA2 changes only marginally, but if the charges on both termini are neutralized (Ac-NV9-NH2), the peptide binding is greatly reduced. The corresponding Kd,low is shown for respective peptides. b Representative charge-deconvoluted spectra of the distinct protein and protein–peptide complex species recorded at 10 V. Olive and dark green correspond to the free β2m domain and heavy chain respectively. Teal corresponds to a free heavy chain still attached to a peptide. The different complexes are assigned in yellow (empty dsA2), coral (dsA2/erucamide), light blue (dsA2/pep), and dark blue (dsA2/pep/pep).
