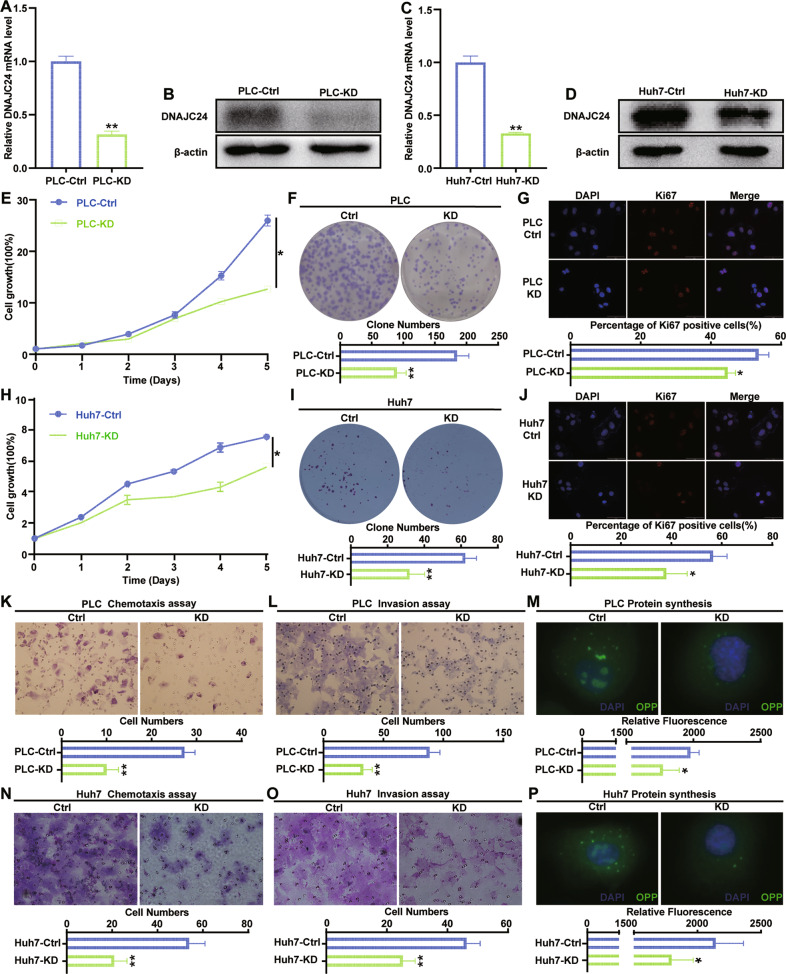
Fig. 4. Knockdown of DNAJC24 inhibits proliferation, motility, and protein synthesis in HCC cells in vitro.
A, C PLC and Huh7 cells were infected with a lentivirus to produce stable DNAJC24 knockdown (KD) cells. qRT-PCR was performed to determine levels of DNAJC24 mRNA. β-actin was used as an internal control. B, D Western blotting was performed to determine levels of DNAJC24 protein. E, H CCK-8 cell viability assay analysis of the impact of DNAJC24 knockdown on PLC (E) and Huh7 (H) cell growth. Results were normalized to viability at day 0 and represented as fold change. F, I Colony formation assay showing the effects of DNAJC24 knockdown on PLC (F) and Huh7 (I) cell growth. G, J Immunofluorescence staining detected Ki67 expression in DNAJC24-KD cells and control cells. Representative images and Ki67 positive cell rates are as shown. K, L, N, O Chemotaxis (K, N) and Matrigel invasion (L, O) assays were used to detect the effect of DNAJC24 knockdown on PLC (K, L) and Huh7 (N, O) motility. M, P Newly synthesized protein was detected in PLC (M) and Huh7 (P) cells after DNAJC24 knockdown using a protein synthesis assay kit. Data were presented as mean ± SEM. n = 2–3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.