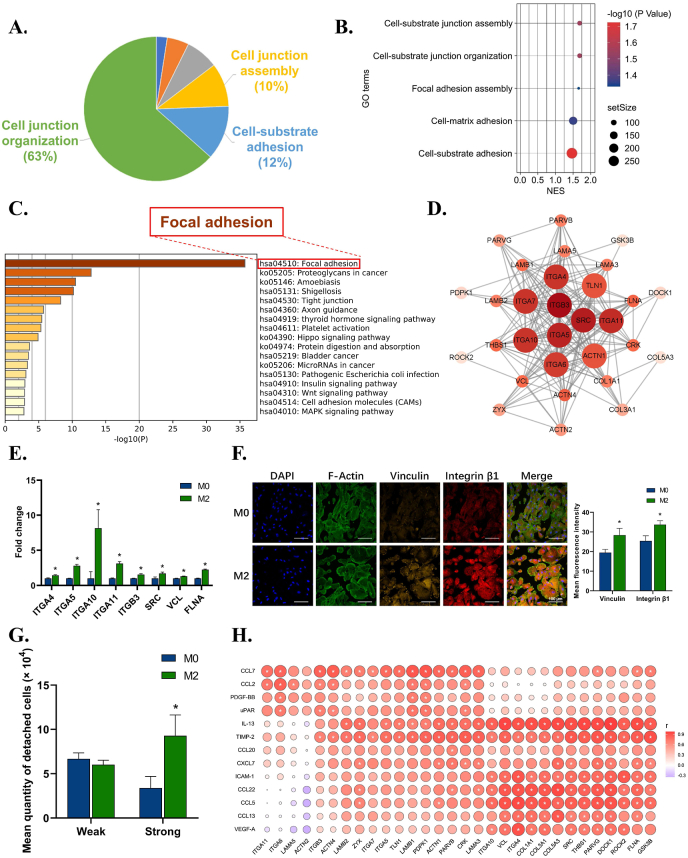
Fig. 3.
The effects of macrophage immune microenvironment on the pro-tissue material adhesion function of fibroblasts. A) Leading terms analysis reveals components of the adhesion clusters, with cell-substrate adhesion at top 2. B) GO terms reveals subterms in cell-substrate adhesion components. C) KEGG analysis of cell-substrate adhesion components reveals focal adhesion is the most significant pathway in cell-substrate adhesion. D) Hub gene analysis of focal adhesion pathway in M2 group. E) RT–qPCR results confirm the up-regulation of genes related to focal adhesion. F) Representative immunofluorescence images and semi-quantitative statistical analysis of VCL and integrin β1 expression of fibroblasts in M2 group. G) Cell adhesion assay reveals an increasing percentage of strong adhesion cells in M2 group. H) Correlation analysis between up-regulated cytokines of M2 immune microenvironment and up-regulated focal adhesion-related genes of fibroblast. Data are presented as means ± SD; *p < 0.05.