Fig. 1: Overview of allele-specific copy number estimation of single-cells with Alleloscope.
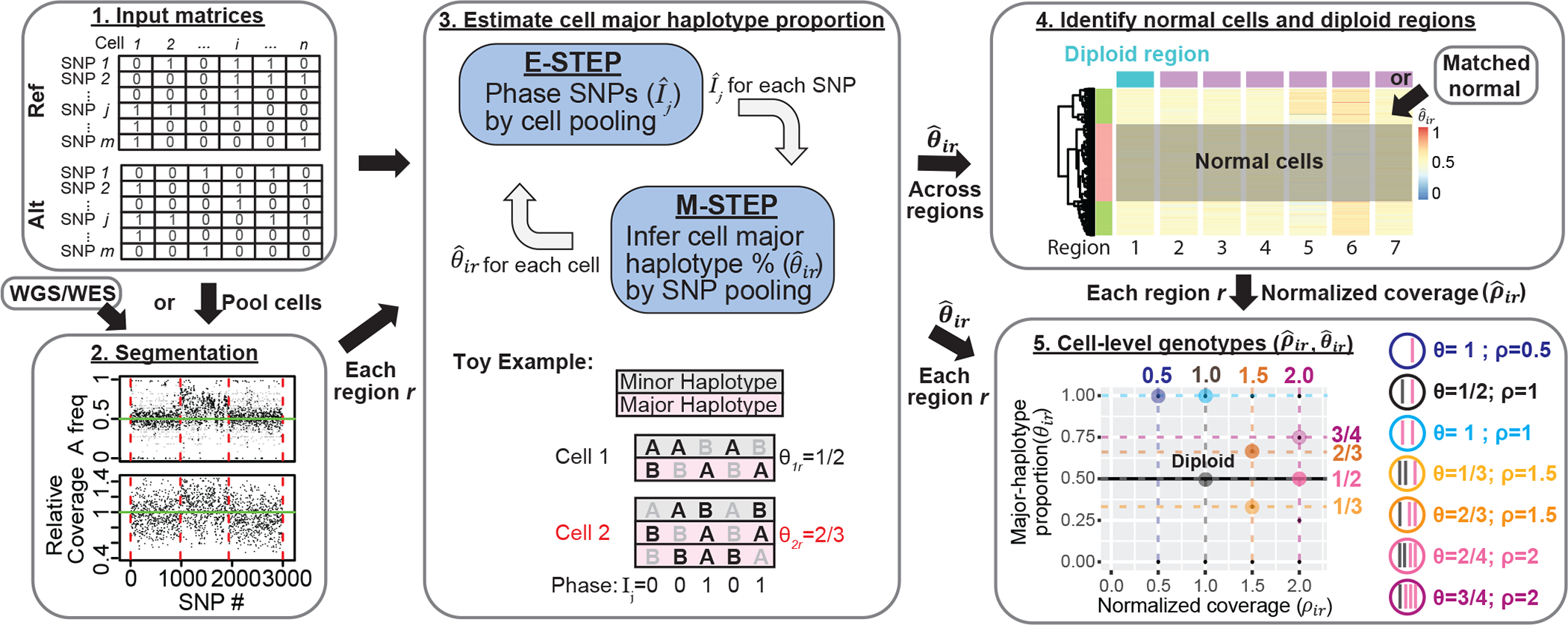
1. The algorithm operates on raw read count matrices for reference allele (Ref) and alternative allele (Alt) computed from single-cell DNA or ATAC sequencing. 2. First, we obtain a segmentation of the genome based on sample-matched whole genome or whole exome sequencing data using FALCON5. If scDNA-seq is available, cells can be pooled to derive a pseudo-bulk. 3. We first define as the major haplotype proportion for cell i for region r derived from the segmentation. Then for each region r, Alleloscope simultaneously phase SNPs () and estimate cell major haplotype proportion () by expectation maximization (EM) algorithm. In the E-step, information is pooled across cells to estimate the phasing of each SNP. In the M-step, information is pooled across all SNPs in the region are pooled to estimate the major haplotype proportion for each cell. The toy example shows a scenario with two cells for a region containing 5 SNPs, with cell 2 carrying an amplification of the major haplotype (in pink). For each cell and each SNP, alleles that are observed in a sequenced read are bolded in black (we assume that only one read is observed, reflecting the sparsity of the data). The true phase (Ij) of the SNPs and the true major haplotype proportion (θir) are shown. 4. After are estimated for each region ’s are pooled across all regions to identify candidate normal cells and candidate normal regions for computing a normalized coverage for region r in cell i. Matched normal can be specified if available. 5. Alleloscope assigns integer allele-specific copy numbers to each cell for each region based on the () pairs.
