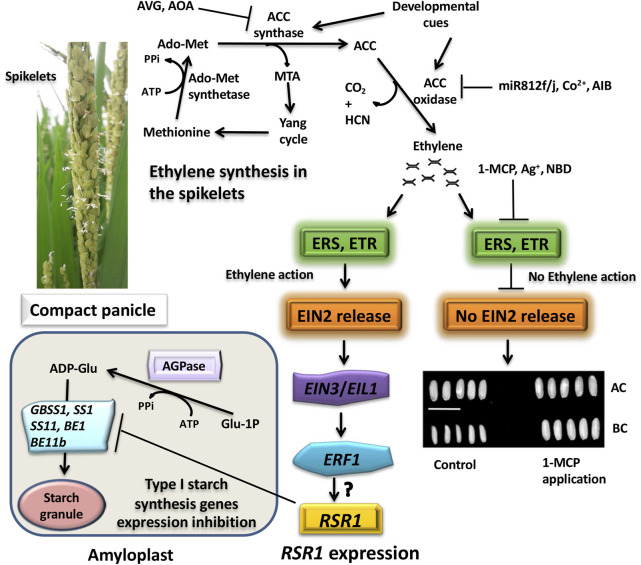
FIGURE 9.
Pictorial presentation of ethylene biosynthesis and ethylene action. Ethylene is synthesized from methionine by the action of ACC synthase that forms ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carbooxylic acid), which is catalyzed by ACC oxidase (ACO) to yield ethylene and HCN as the byproduct. Methionine is regenerated via the Yang cycle. Ethylene action leads to the synthesis of Rice Starch Regulator1 (RSR1), which reportedly inhibits the expression of the type I starch-biosynthesizing enzymes, leading to inhibition of starch biosynthesis and poor grain filling. Inhibition of ethylene synthesis by AVG (2-aminoethoxyvinyl glycine), AOA (2-aminoooxyacetic acid), AIB (aminoisobutyric acid), Co2+, and the miRNAs miR812f/j and blocking of the ethylene action by the use of ethylene receptor blockers like 1-MCP (1-methylcyclopropene), Ag+, and NBD (2,5-norbornadiene) lead to no ethylene action resulting in proper filling of the grain. MTA, methylthioadenine; Ado-Met, adinosyl-methionine; ERS, ETR, ethylene receptors; AC, apical caryopses; BC, basal caryopses.