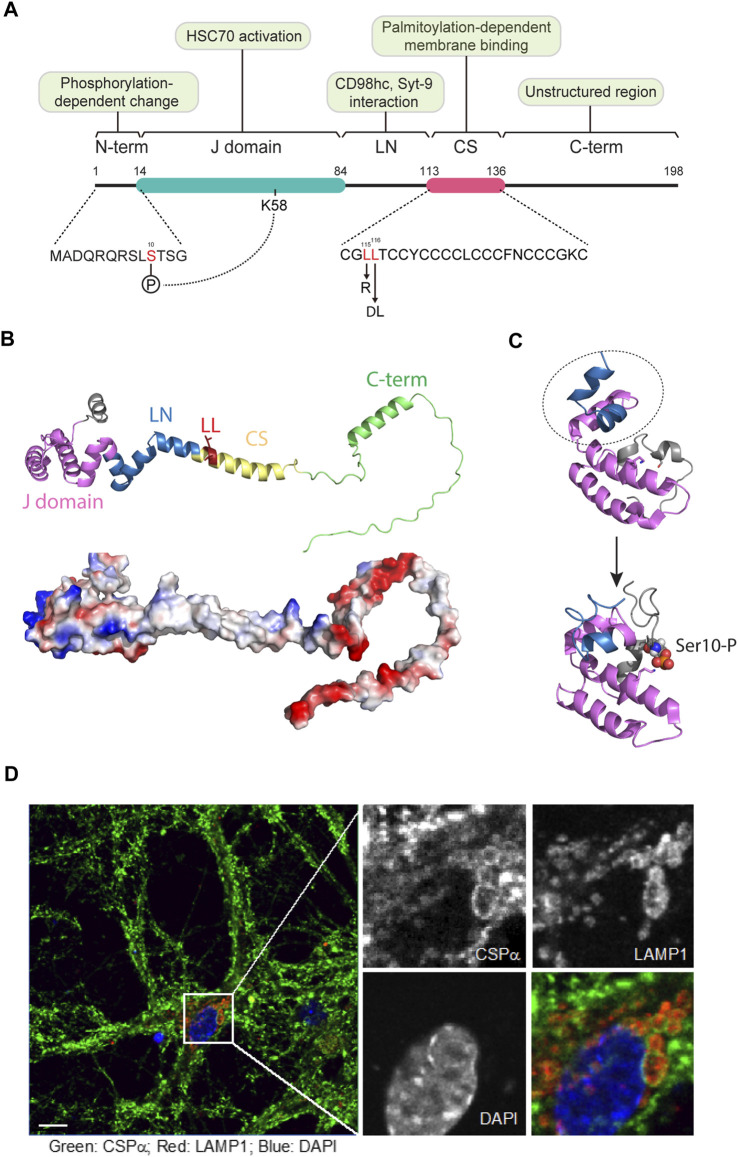
FIGURE 1.
The structure and subcellular localization of CSPα. (A) The domain structure of CSPα. CSPα consists of 5 domains, a small N-terminal (N-term.) segment, a DnaJ (J) domain, a hydrophobic linker (LN), a cysteine string (CS) domain, and a disordered C-term domain. Phosphorylation at Ser10 in the N-domain by PKA or PKB may allow CSPα activation by forming an intramolecular interaction between p-Ser10 and Lys58 in the J domain. The conserved J domain is essential for HSC70 interaction and activation. The LN domain can interact with other proteins such as Synaptotagmin-9 and CD98hc, which regulate SNARE complex assembly and MAPS, respectively. The CS domain possesses 14 cysteine residues for palmitoylation, engaging CSPα to membrane compartments. Mutations in two leucine residues (L115R and ΔL116) within the CS domain are linked to ANCL disease. (B) Upper panel, A ribbon model of full length human CSPα predicted by Alphafold (Identifier, AF-Q9H3Z4-F1). Each domain is labeled in colors. N-terminal domain, grey; J domain, pink; LN domain, blue; cysteine-string, yellow; C-terminal domain, light green. The ANCL-linked mutations in the CS domain are highlighted in red. Lower panel, a surface electrostatic potential view of the CSPα Alphafold model. (C) A phosphorylation dependent conformational change in the CSPα J domain as revealed by NMR. PDB: 2N04 and 2N05. Notice that the subdomain labeled in dashed oval rotates down to pack on the other subdomain labeled in magenta when Ser10 is phosphorylated. (D) The subcellular localization of CSPα in primary neurons. Murine primary hippocampal neurons at DIV10 were stained by antibodies for CSPα (green) and the lysosomal marker LAMP1 (red). Note that CSPα in Soma is localized to vesicular structures that overlap with LAMP1. Nuclei were labeled by DAPI in blue. Scale bars, 10 µm.