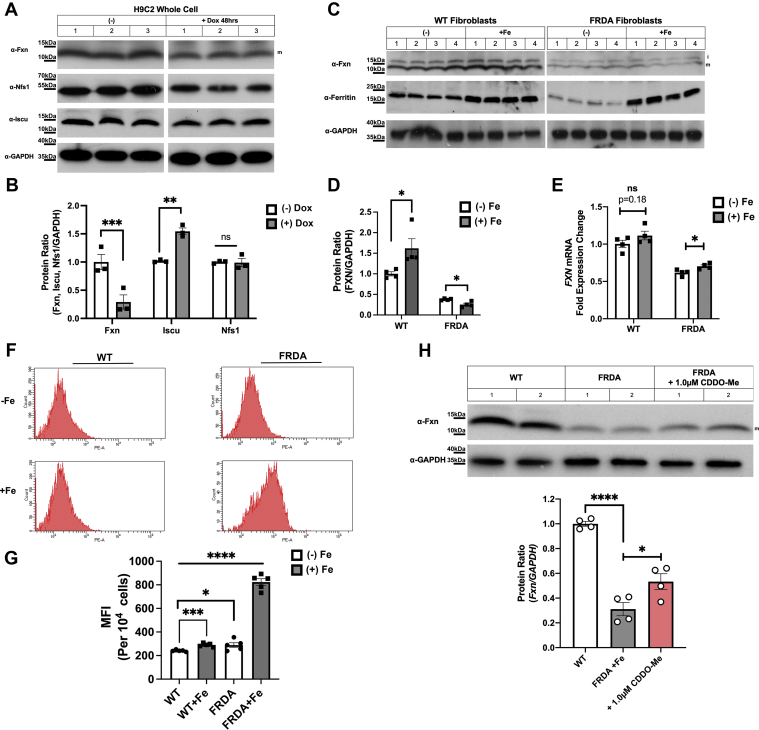
Figure 3.
Frataxin levels are reduced in doxorubicin exposed cardiomyocytes and FRDA fibroblast exposed to increased iron.A, rat H9C2 cells were incubated with or without 10 μM doxorubicin for 48 h, cells were harvested, washed in PBS, lysed in 1% Triton X-100, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris–HCl, 0.5 mM Na4EDTA pH 7.2, 0 °C 30 min, and centrifuged for 30 min at 14,000g. Supernatants were boiled in SDS-PAGE loading buffer, run on 4 to 20 SDS-PAGE and Fxn, Nfs1, Iscu, and GAPDH levels determined by Western blot. A representative blot with three replicates is shown. n = 3 replicate experiments. B, blots from (A) were quantified using GAPDH as a loading control and data normalized to 1.0 using samples without doxorubicin as a control. Error bars represent SEM (n = 3 replicate experiments). C, WT and FRDA fibroblasts were grown in the absence or presence of 20 μM FeNTA for 48 h, harvested, and lysed as described in (A) and Fxn, ferritin, and GAPDH levels determined by Western blot. Representative blots with four experimental replicates are shown. n = 4 replicate experiments. D, Western blots from (C) were quantified as described in Experimental procedures and data normalized to 1.0 using WT samples without FeNTA as the control. Error bars represent SEM (n = 4 replicate experiments). E, FXN and ACTB transcript levels from cells as in (C) were quantified using RT-qPCR as described in Experimental procedures. (n = 4 replicate experiments with 3–4 technical replicates/experiment). F, mitochondrial ROS were determined using MitoSOX in FRDA cells as in (C) with an example graph shown for WT and FRDA ± Fe. G, MitoSOX values from five biologic replicates as in (F) were graphed and expressed as the MFI. H, cells grown in supplemental FeNTA as in (C) were treated with the Lon1 protease inhibitor CDDO-Me (1.0 μM) for 24 h and Fxn and GAPDH levels determined and quantified n = 4 replicate experiments. CDDO, 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid 9; FeNTA, Fe-nitrotriacetic acid; FRDA, Friedreich’s ataxia; Fxn, frataxin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription quantitative PCR.