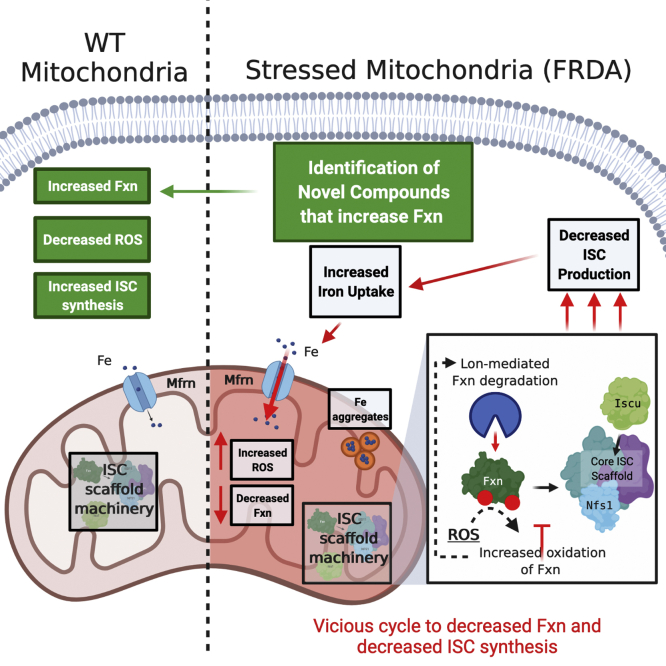
Figure 7.
Graphic abstract of mitochondrial stress and Fxn turnover in FRDA. Under normal conditions WT mitochondria have an intact ISC machinery and iron import into the mitochondrial occurs at a normal rate. In FRDA, with diminished Fxn or when ISC synthesis is diminished, mitochondrial iron import is increased without improvements in ISC synthesis. This causes iron accumulation in the mitochondrial, increased mitochondrial ROS, and decreased Fxn protein levels. We speculated that Fxn is oxidized under these conditions making it susceptible to increased proteolytic degradation in the mitochondria by the Lon protease. We identified novel compounds that increased Fxn levels in FRDA cells that resulted in decreased ROS and increased ISC synthesis. We speculate that these compounds, in combination with other FRDA therapeutics, would delay disease progression. FRDA, Friedreich’s ataxia; Fxn, frataxin; ISC, Fe–S cluster; ROS, reactive oxygen species.