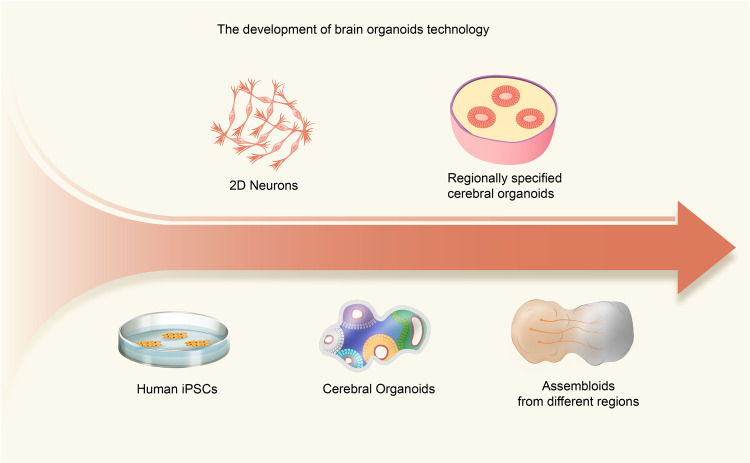
Fig. 3.
Graphical summary of major milestones in the development of brain organoid technologies. The advent of human iPSC (hiPSC) technologies has enabled the production of specialized human cells in large quantities for disease modeling. hiPSCs have been widely available for 2D culture systems, but 3D models are regarded as more advanced alternatives to mimic human brain complexity. Lancaster et al. produced cerebral organoids by embedding embryoid bodies into an extracellular matrix (ECM), giving hiPSCs the most freedom for self-organization; the resulting organoids contained diverse tissues, including the retina, forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, and choroid plexus. However, at the early stage of brain region-specific organoid culture, patterning factors were used to determine the fate of progenitor cells and then removed at the further differentiation stages. These guided protocols allowed the generation of two or more organoids resembling various brain regions that can then be used to fuse to form assembloids, which can be used to simulate the interactions between different brain regions