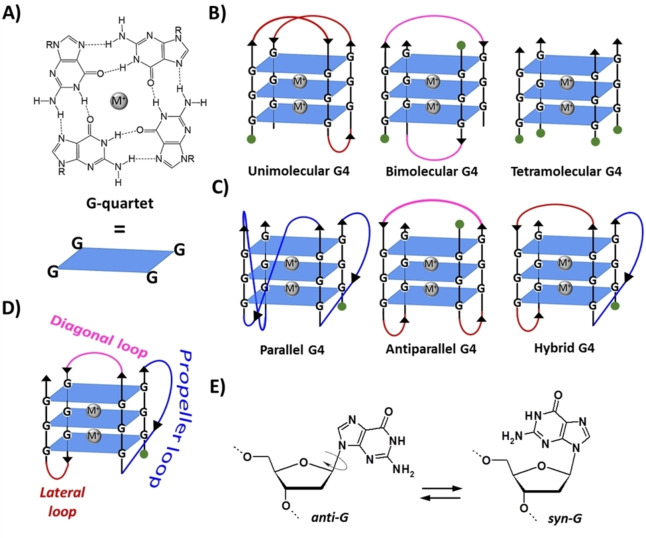
Figure 1.
A) Structure and schematic representation of a G‐quartet. B) Schematic representation of unimolecular, bimolecular and tetramolecular G4s formed by stacking of three G‐quartets. C) Examples of three different topologies of unimolecular G4. D) Types of linking loops in a G4. E) The anti/syn conformations of the 2′‐deoxyguanosine. M+ indicates a stabilizing metal cation, for example K+ or Na+. R=1‐β‐D‐2‐deoxyribofuranosyl group. Green circles indicate the 5’‐end.