FIG. 3.
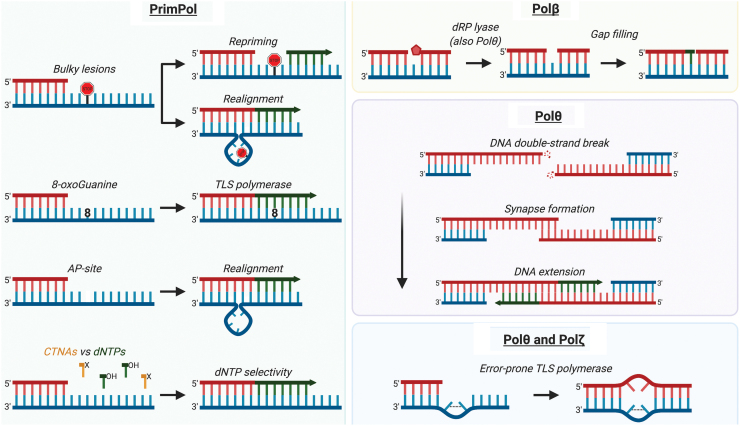
Additional polymerases in the mitochondria. Apart from the replicative Polγ, mitochondria also contain TLS polymerases to assist mtDNA replication and repair processes. The biochemical activities performed by these polymerases are depicted, but whether some activities occur in the mitochondria in vivo still lacks evidence. Primpol is primarily believed to rescue stalled replication forks by repriming ahead of the damage (e.g., UV-lesions, G-quadruplexes, blocking agents). PrimPol is a versatile DNA primase-polymerase that can bypass small lesions such as 8-oxodG by acting as a TLS polymerase or, alternatively, performing primer/template realignment based in sequence microhomology past “unreadable” damage (e.g., AP-sites, bulky lesions). It also presents higher discrimination than Polγ against CTNAs. Polβ, such as Polθ, can perform DNA-end processing through its 5′-dRP lyase activity. Polβ is a specialized gap-filling polymerase, acting mainly in BER. In the nuclei, Polθ is implicated in the repair of DNA DSBs mediated by sequence microhomology (MMEJ), although a role in mitochondrial DSB repair remains to be demonstrated. Polθ promotes DNA synapse formation between single-strand DNA overhangs, followed by DNA extension. Polθ and Polζ are known error-prone TLS polymerases that are able to bypass more mutagenic lesions (e.g., AP-sites, thymine glycol, UV-lesions) by inserting nucleotides opposite them or extending a lesion-containing mismatch. AP, apurinic or apyrimidinic; BER, base excision repair; CTNA, chain-terminating nucleoside analog; dRP, deoxyribose phosphate; MMEJ, microhomology-mediated end joining; TLS, translesion synthesis. Color images are available online.