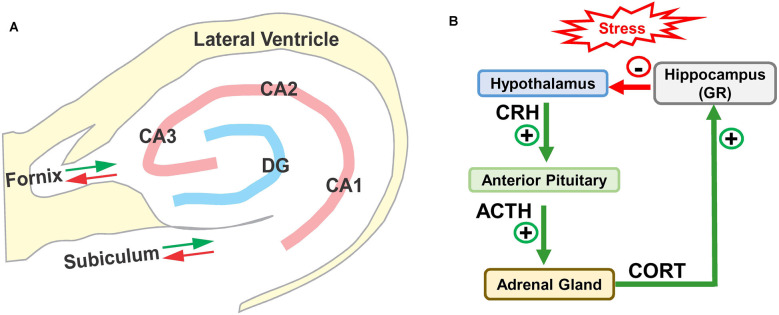
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic of hippocampus and surrounding lateral ventricle. Three subdivisions of the rodent Cornu Ammonis (CA1, CA2, and CA3) surrounding the dentate gyrus (DG). Only the major afferent and efferent pathways (red/green arrows) through the subiculum and fornix are shown. (B) Schematic of hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis with hippocampus. Stress stimulates the release (+) of corticotropic releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus, which binds to receptors in anterior pituitary causing the release (+) of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) which stimulates the release of corticosterone (CORT). CORT binds to glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) in the hippocampus, which provides negative feedback (−) to the hypothalamus suppressing the release of CRH, ACTH, and CORT.