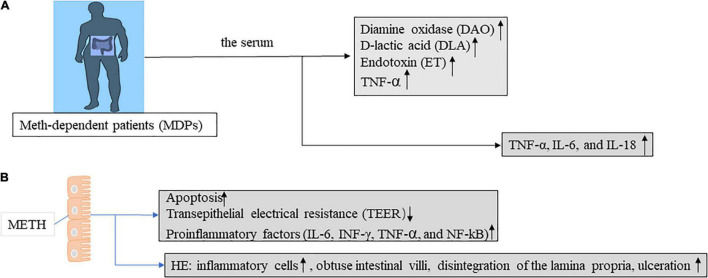
FIGURE 2.
Intestinal barrier function was evaluated in mice and humans in the context of METH treatment. (A) Intestinal mucosal injury, intestinal wall permeability, and bacterial translocation are assessed by determining the serum levels of diamine oxidase (DAO), D-lactic acid (DLA), and endotoxin (ET) in Meth-dependent patients (MDPs). Abnormal levels of all these indicators reflect intestinal barrier dysfunction. (B) Intestinal epithelial cells of methamphetamine-treated mice are evaluated for intestinal barrier function by apoptosis, TEER, proinflammatory factors, and HE staining. Abnormal levels of all these indicators reflect intestinal barrier dysfunction.