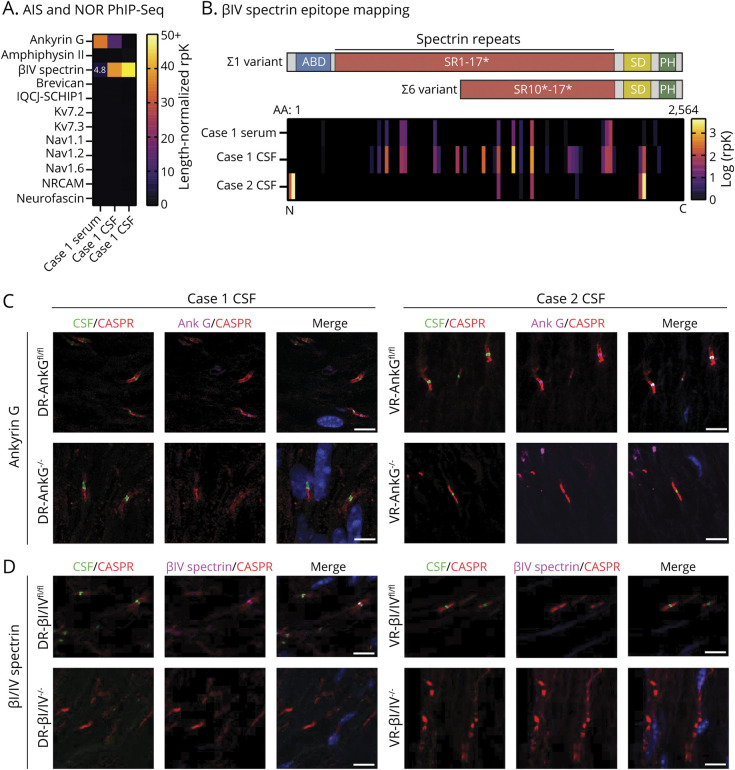
Figure 2. Identification and Validation of Anti–BIV-Spectrin Antibodies.
(A) Heatmap of PhIP-Seq enrichments of proteins expressed in the both AIS and NoR. Enrichments are represented as length-normalized rpK (total rpK for the given protein/number of peptides that map to that protein, see supplemental methods). βIV-spectrin was detected in case 1 CSF with a length-normalized rpK = 4.8. All dark and unmarked cells had a length-normalized rpK <1. (B) Graphical representation of the approximate and relative locations of actin-binding domain (ABD, blue), spectrin repeats (SR, red, * = partial SR), specific domain (SD), and pleckstrin homology domain (PH, green) relative to PhIP-Seq peptide enrichments in the heatmap below spanning the full length of βIV-spectrin (amino acids 1–2564, overlapping peptides are laid end-to-end). Heatmap of βIV-spectrin peptide enrichments regarding AIS and nodal βIV-spectrin isoforms Σ1 and Σ6. Each peptide corresponds to a single peptide. N and C refer to the amino and carboxy termini of βIV-spectrin. (C) Left, case 1 CSF immunostaining of AdvillinCre/+ DR-AnkGfl/fl and DR-AnkG−/− shows nodal staining in the absence of AnkG, suggesting that AnkG is not the autoantigen. Right, case 2 CSF immunostaining of ChatCre/+ VR-AnkGfl/fl and VR-AnkG−/− tissue indicates that case 2 does not harbor AnkG antibodies. (D) Case 1 and 2 CSF immunostaining of AdvillinCre/+ DR-βI/βIVfl/fl and DR-βI/βIV−/− shows the disappearance of nodal staining in the absence of βI/V-spectrin, suggesting that βIV-spectrin is the autoantigen in both cases. For C and D, CSF was immunostained at 1:4 dilution. All scale bars = 5 µm. AIS = axon initial segment; AnkG = ankyrin G; IgG = immunoglobulin G; NoR = node of Ranvier; PhIP-Seq = phage display immunoprecipitation sequencing.