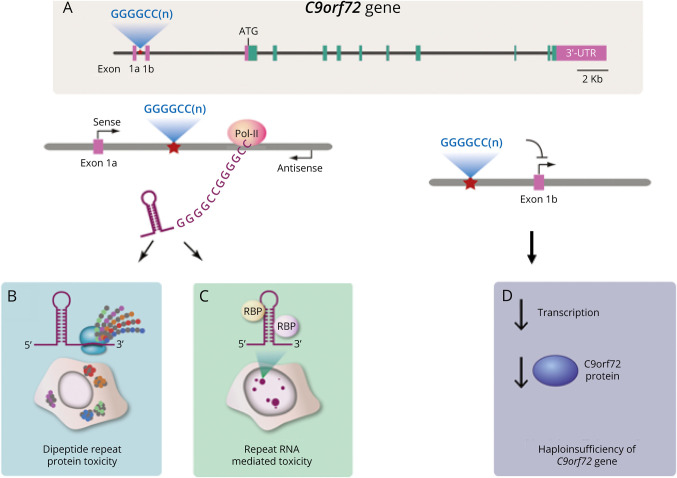
Figure 1. Proposed Mechanisms of C9ORF72 Expansion.
(A) The C9ORF72 gene contains a polymorphic hexanucleotide (GGGGCC) repeat in a noncoding region. (B) RNA transcripts with the C9ORF72 repeat expansions are produced by both sense and antisense transcription, resulting in the accumulation of nuclear and cytoplasmic aggregation of both sense and antisense repeat-containing RNA. Repeat-containing RNA can cause sequestration of essential RNA-binding proteins leading to defects in pre-mRNA splicing. (C) Expansion repeat is a substrate for non–ATG-dependent translation event that generates dipeptide repeat proteins that cause toxicity through aggregation and altering multiple essential cellular functions. (D) Repeat expansion can interfere with transcription and cause downregulation of C9ORF72 gene expression and loss of C9ORF72 protein function. Adapted from Gitler et al. There has been an awakening: Emerging mechanisms C9orf72 mutations in FTD/ALS. Brain Res. 2016;1647.