FIGURE 2.
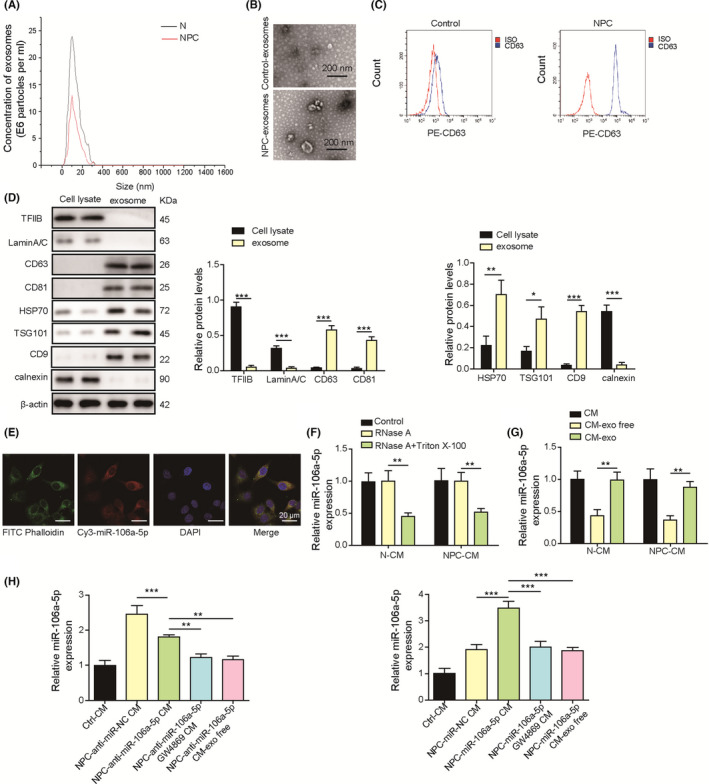
Exosome‐derived miR‐106a‐5p entered nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells. A, The size of exosomes isolated from conditioned media (CMs) derived from NPC and normal cells was examined by dynamic light scattering (DLS). B, Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis of exosomes derived from normal nasopharyngeal and NPC tissues. C, CD63 expression on exosomes was examined by flow cytometry. D, Protein levels of TFIIB, LaminA/C, CD9, CD63, CD81, Hsp70, and TSG101 in cell lysates and exosomes. E, Exosomes were isolated from CAFs transfected with Cy3‐labeled miR‐106a‐5p mimics (red) and incubated with SUNE‐1 cells. DAPI (blue) and phalloidin (green) were used for nuclear and F‐actin staining (magnification, 500×; scale bar, 20 µm). F, RT‐qPCR analysis of miR‐106a‐5p in N‐CM and NPC‐CM treated with RNase A or RNase A plus Triton X‐100 (n = 3). G, RT‐qPCR analysis of miR‐106a‐5p in N‐CM, NPC‐CM, exosomes from N‐CM or NPC‐CM (CM‐exo), and exosome‐depleted CM (CM‐exo free, n = 3). H, RT‐qPCR analysis of miR‐106a‐5p in SUNE‐1 cells cultured in control N‐CM (Ctrl CM), NPC‐CM plus miR‐106a‐5p inhibitor NC (NPC‐anti‐miR‐NC CM), NPC‐CM plus miR‐106a‐5p inhibitor (NPC‐anti‐miR‐106a‐5p CM), NPC‐CM plus miR‐106a‐5p inhibitor/GW4869 (NPC‐anti‐miR‐106a‐5p GW4869 CM), and NPC‐CM exo free plus miR‐106a‐5p inhibitor (NPC‐anti‐miR‐106a‐5p CM exo free). **p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001
