Fig. 3.
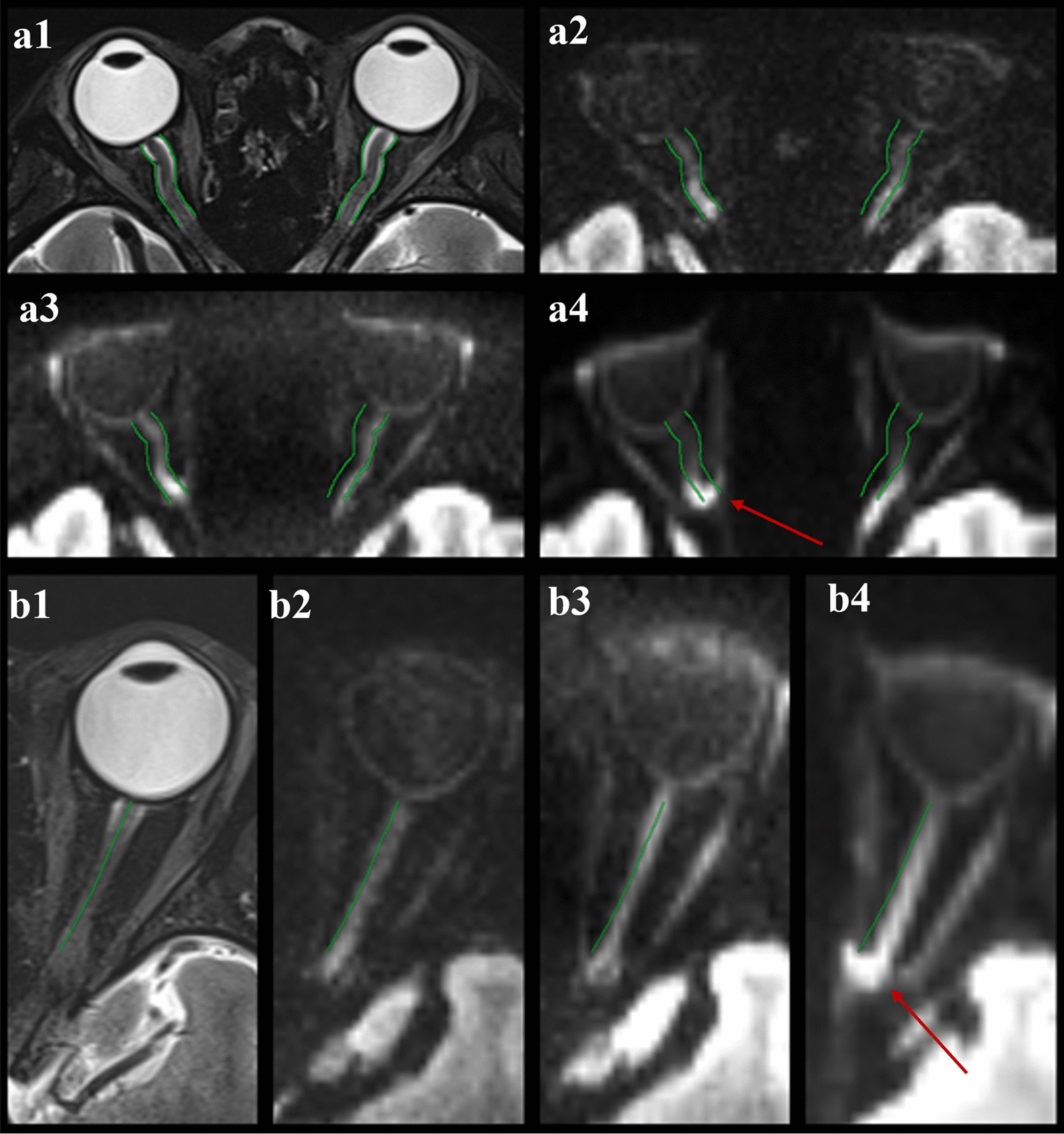
Examples of image quality and distortion of three DW techniques. a Imaging in a 28-year-old female volunteer. a1–a4 images of T2w, rs-EPI DWI at b value = 1000 s/mm2, rFOV-EPI DWI at b value = 1000 s/mm2 and ss-EPI DWI at b value = 1000 s/mm2, respectively. b Imaging in a 25-year-old female volunteer. b1–b4 images of T2w, rs-EPI DWI at b value = 1000 s/mm2, rFOV-EPI DWI at b value = 1000 s/mm2 and ss-EPI DWI at b value = 1000 s/mm2, respectively. Note the improved image quality and markedly reduced susceptibility distortions in the rs-EPI and rFOV-EPI sequences compared with ss-EPI. There are severe distortions due to the susceptibility artifacts caused by the air-bone-tissue interface on ss-EPI DWI (arrows in a4, b4). rs-EPI DWI, readout-segmented echo-planar imaging diffusion-weighted imaging; rFOV, reduced field-of-view; ss-EPI, single-shot echo-planar imaging
