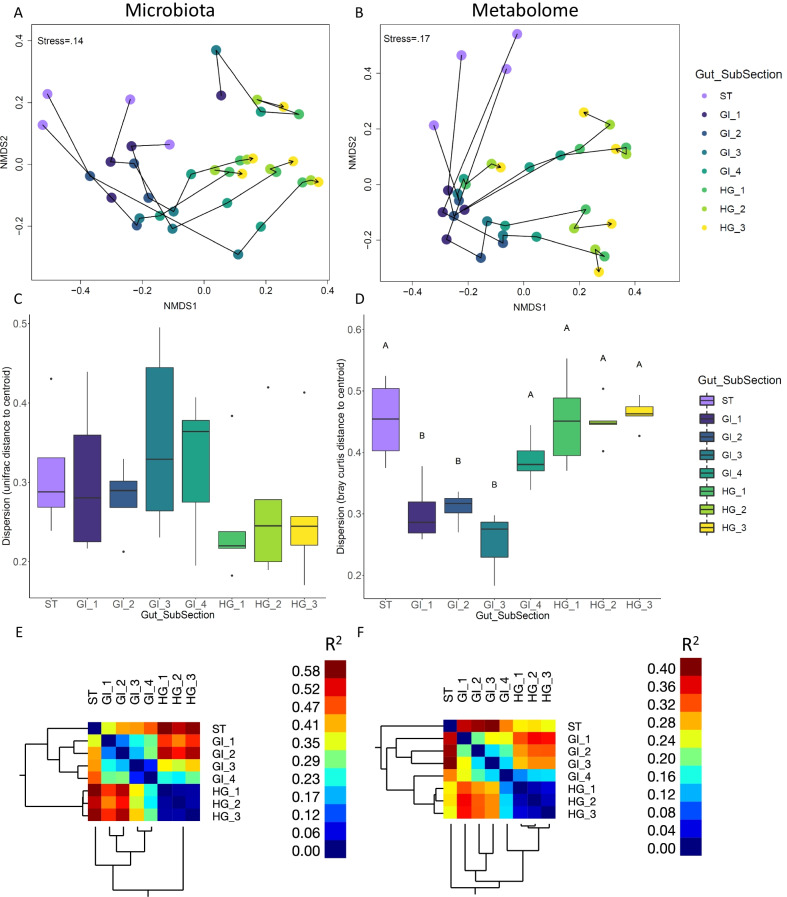
Fig. 2.
Microbial (A, C, E) and metabolomic (B, D, F) multivariate analysis of nenue gut subsections. Non metric multidimensional scaling plots of the weighted unifrac distances among microbial communities (A) and bray Curtis distances among metabolomic samples (B) from the nenue gut. Samples are colored by gut subsection. Arrows track the transition of microbiota/metabolomes in an individual fish, starting in the stomach and ending in the hindgut. Box and whisker plots depict multivariate dispersion of microbial communities (unifrac distance to centroid) (C) and metabolomic samples (bray curtis distance to centroid) (D). Samples are color coded by gut subsection. Dispersion in both microbial communities and metabolomic samples responded significantly to gut subsection, but only metabolomic samples showed significant post hoc pairwise differences (α = .05, Tukey Post Hoc test), which are indicated by letter significance indicators. Clustering heatmaps depict pairwise R2 values between samples from PERMANOVAs for (E) microbiota and (F) metabolome datasets