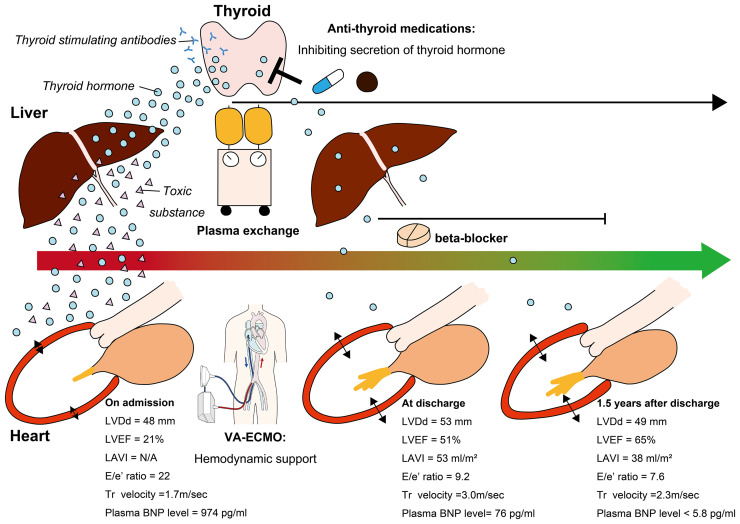
Figure 3.
Treatments, clinical time course, and proposed mechanism of illness resolution. This patient underwent plasma exchange to remove excessive thyroid hormone, cardio-depressants, thyroid-stimulating autoantibodies, and toxic substances generated due to liver dysfunction. Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was also performed to maintain haemodynamics during the cardio-depressive state. Both procedures were well tolerated. Simultaneously, anti-thyroid medications and a beta-blocker were administered to control secretion of thyroid hormone and prevent it from affecting downstream organs, including the heart. The patient could be weaned from veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation following plasma exchange. Close follow-up enabled normalization of cardiac structure and function by optimizing medical therapy for hyperthyroidism and beta-blocker treatment for heart failure. BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; LAVI, left atrial volume index; LVDD, left ventricular end-diastolic dimension size; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; Tr, tricuspid regurgitation; VA-ECMO, veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.