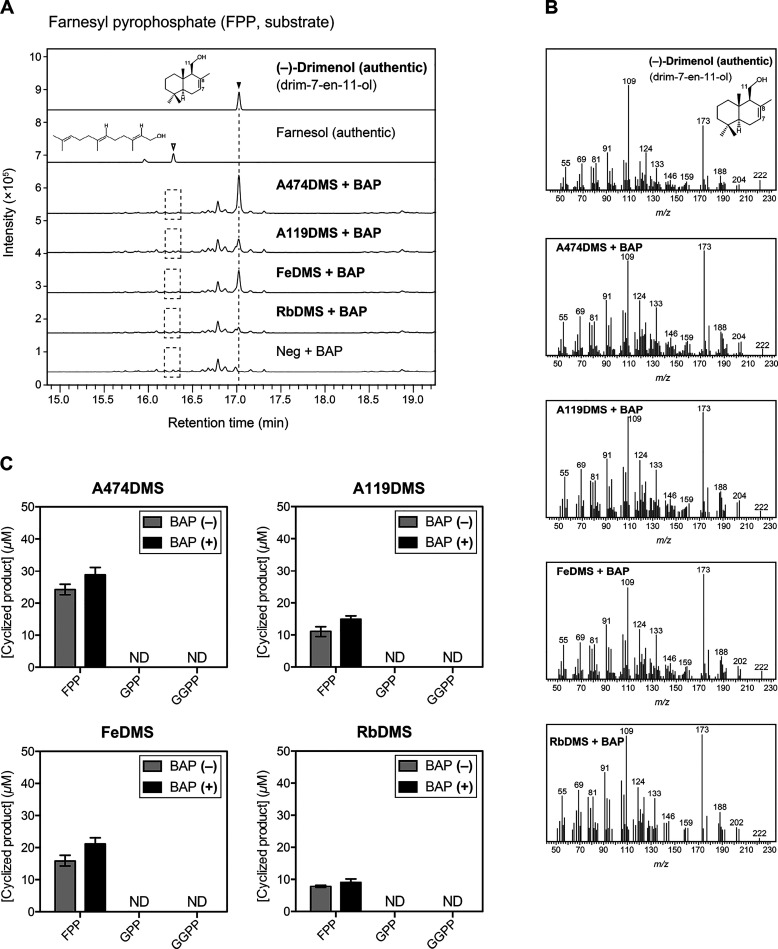
Figure 3.
Catalytic activity of the four recombinant proteins A474DMS, A119DMS, FeDMS, and RbDMS. (A) GC–MS chromatograms of the authentic (−)-drimenol (drim-7-en-11-ol) and farnesol compounds and in vitro reaction products. The enzymatic assays of each purified protein were performed individually in the presence of FPP as a substrate, with or without alkaline phosphatase (BAP) treatment. The reactions in the absence of protein (Neg) were used as negative controls. (B) Mass spectra of the authentic (−)-drimenol and each reaction product detected in (A). The GC–MS data in (A,B) represent three independent reactions performed with the same preparation of each purified protein. Dashed boxes indicate that no desired reaction products were detected. (C) Comparison of the substrate selectivity of A474DMS, A119DMS, FeDMS, and RbDMS proteins. The enzyme reactions of each protein were performed individually under the same conditions as in (A), except for the inclusion of additional substrates: GPP, geranyl pyrophosphate, and GGPP, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. Data are the means ± SD of three independent experiments performed with the same preparation of each purified protein. ND, not detectable; A474, Aquimarina sp. AU474; A119, Aquimarina sp. AU119; Fe, F. eckloniae; Rb, Rhodobacteraceae KLH11; and m/z, mass-to-charge ratio.