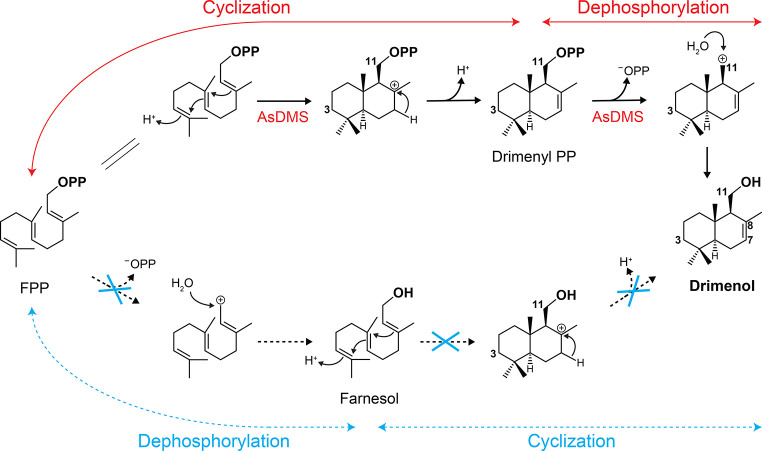
Figure 4.
Proposed mechanism of drimenol biosynthesis catalyzed by the bifunctional AsDMS. Protonation at C3 mediated by the DxDTT motif occurs first, followed by double-bond rearrangements and deprotonation to produce drimenyl pyrophosphate (the cyclization step). Next, cleavage of the diphosphate group by the DDxxE motif and Mg2+ ions generates carbocation, which could be quenched by a water molecule to produce drimenol (the dephosphorylation step).