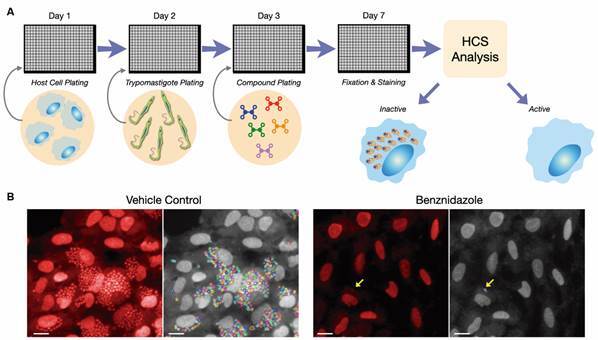
Fig. 3: high content screening (HCS) for the discovery of anti-Trypanosoma cruzi compounds. (A) Schematic representation of a general HCS assay setup. Host cell lineage and T. cruzi strains of choice can vary significantly between laboratories and assays. Infected cells are exposed to compounds post-infection for a defined period of time and then antiparasitic activity is evaluated against intracellular amastigotes. Microplates are processed for image analysis. Highly active compounds will result in the (nearly complete) clearance of intracellular amastigotes. (B) Typical images of T. cruzi-infected cells treated with vehicle (left) and an efficacious concentration of benznidazole (right). Raw images are shown in red-stained host cell and parasite, and one key feature of HCS automated image analysis, amastigote segmentation and quantification, is shown in colored lines over grey-colored cells. While efficacious, benznidazole cannot often clear all intracellular amastigotes during short exposure times, and some amastigotes might remain after treatment (arrows).