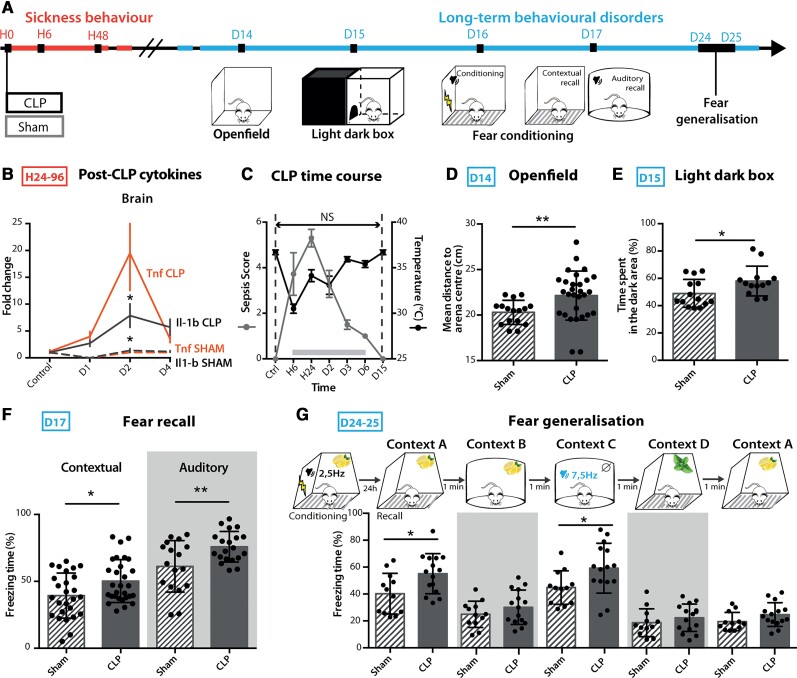
Figure 1.
CLP mice developed long-term anxiety and PTSD-like conditioned fear expression. (A) Timeline of the experiment: long-term anxiety and fear-related behaviours were tested from 2 weeks post-surgery. (B) Brain cytokine levels were significantly increased post-CLP [ncontrol = 5, nD1-sham = 1, nD1-CLP = 5, nD2-sham = 4, nD2-CLP = 8, nD3-sham = 5, nD3-CLP = 5. IL1-b: group F(1,30) = 2.931, P = 0.0972, D2: *P = 0.0119; TNF: group F(1,30) = 7.354, *P = 0.0110, D2: *P = 0.0141]. (C) CLP-induced sickness behaviour (nControl = 9, nCLP = 90) was transient and totally disappeared at D15. (D and E) CLP caused long-term anxiety behaviour illustrated by an increased mean distance to arena centre in the open field (D; nSham = 16, nCLP = 23, **P = 0.0037) and an increased time spent in the dark area during the light/dark box test (E; nSham = 14, nCLP = 13, *P = 0.0348). (F) Twenty-four hours after aversive conditioning, CLP mice displayed an enhanced freezing behaviour during both contextual and auditory fear conditioning recall (Contextual: nSham = 27, nCLP = 29, *P = 0.0176; Auditory: nSham = 18, nCLP = 20, *P = 0.0108). (G) CLP mice showed an increased freezing behaviour when confronted to stimuli partially related to the conditional stimulus in the generalization test [nSham = 12, nCLP = 15, group, F(1,25) = 9.243, **P = 0.0055; Context A, *P = 0.0136; Context C, *P = 0.0183]. Statistics: (D–F) Mann–Whitney test or unpaired t-test; (B, C and G) two-way ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparison tests (grey bar when significant). Data shown as mean ± SD. D = days post-surgery; H = hours post-surgery.