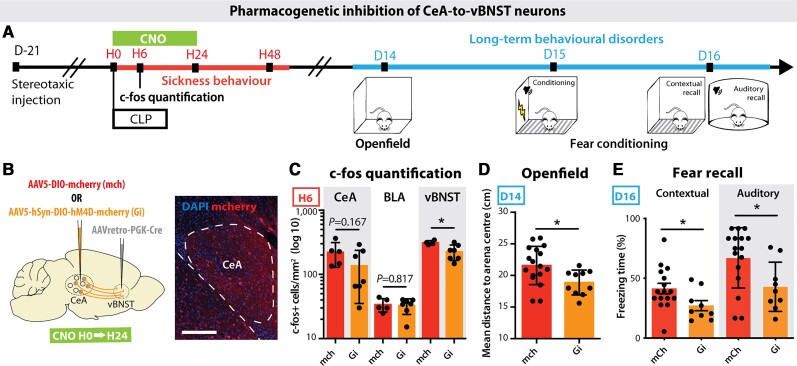
Figure 7.
Transient pharmacogenetic silencing of vBNST-projecting CeA neurons prevents the development of anxiety and PTSD-like conditioned fear expression. (A) Timeline of the experiment. Three weeks after stereotaxic injection of viral vectors, mice underwent a CLP and were injected with clozapine N-oxide (CNO) during the 24 h following surgery. Long-term behaviour was then tested 15 days post-surgery. (B) A retrograde Cre-expressing virus was injected in the vBNST and a Cre-dependent inhibitory DREADD (Gi) or mCherry control (mch) virus was injected in the CeA to allow the recombination and the expression of the Gi/mch viruses exclusively in the vBNST-projecting CeA neurons. (C) H6 c-fos quantification showed an inhibiting effect of Gi over the post-CLP neuronal activation in the vBNST compared to mCherry controls, with no impact on other neighbouring regions such as the BLA (nmch = 5, nGi = 7, vBNST: *P = 0.0257). (D and E) CNO-induced Gi inhibition for 24 h post-CLP is sufficient to abolish the long-term behavioural changes observed in the open field test (D; nmch = 17, nGi = 10, *P = 0.0190) and the fear conditioning (FC) recall (E; nmch = 16, nGi = 9, Contextual: *P = 0.0415; Auditory: *P = 0.0228). Scale bar = 200 μm. Statistics: Mann–Whitney test or unpaired t-test. Data shown as mean ± SD.