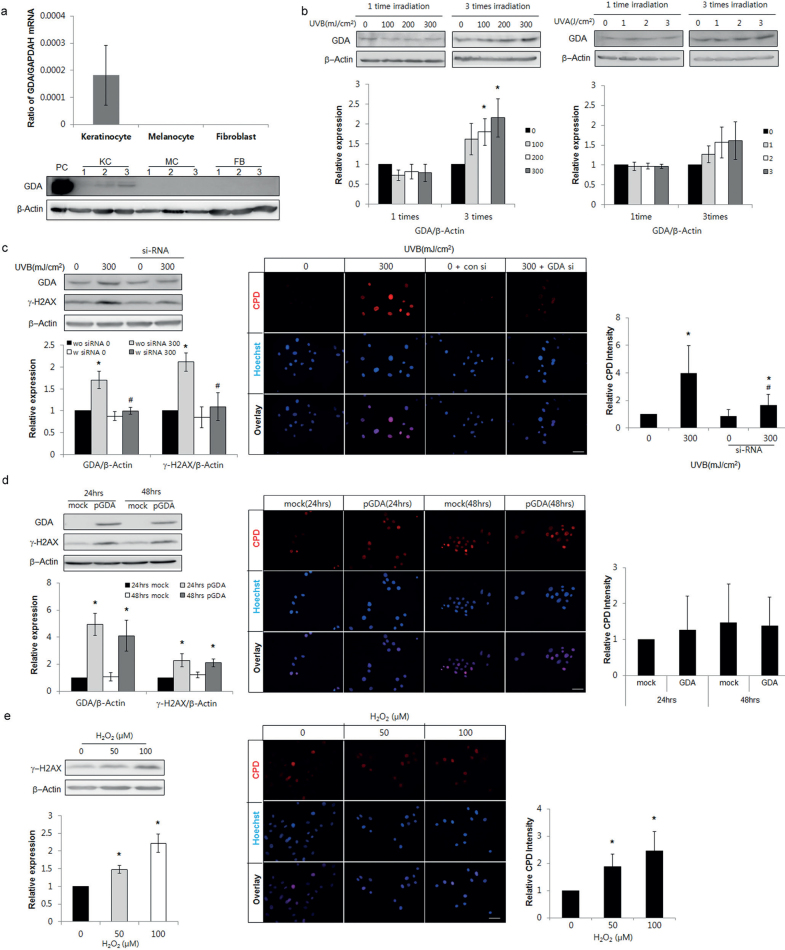
Fig. 2.
Repeated exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation increased guanine deaminase (GDA) in keratinocytes and DNA damage including anti-cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) formation, which was undetected with GDA or reactive oxygen species (ROS). (a) Real-time PCR and western blot analysis of the relative ratios of GDA mRNA and protein levels in primary cultured normal human skin keratinocytes (KCs), melanocytes (MC), and fibroblasts (FB) obtained from 3 different subjects. KC overexpressing GDA were used as positive controls (PC). (b) Western blot of the relative ratios of GDA protein expression in KCs exposed to UVB or UVA irradiation once or 3 times. (c, d) Western blot analysis for the relative ratios of γ-H2AX levels and immunofluorescent staining using anti-CPD antibody in KCs with or without UVB irradiation (300 mJ/cm2, 3 times) and GDA knockdown (c) or GDA overexpression (d). (e) Western blot analysis of the relative ratios of γ-H2AX protein and immunofluorescent staining using anti-CPD antibody in KCs with or without H2O2 treatment. β-Actin and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were used as internal controls for western blot analysis and real-time PCR, respectively. During immunofluorescent staining, nuclei were counter-stained with Hoechst 33258 (bar 0.05 mm) and staining intensities were measured using Wright Cell Imaging Facility (WCIF) ImageJ software. Data represent means ± standard deviation (SD) of 3-4 independent experiments. *p < 0.05 vs. control keratinocytes, #p < 0.05 vs. UV-exposed keratinocytes.