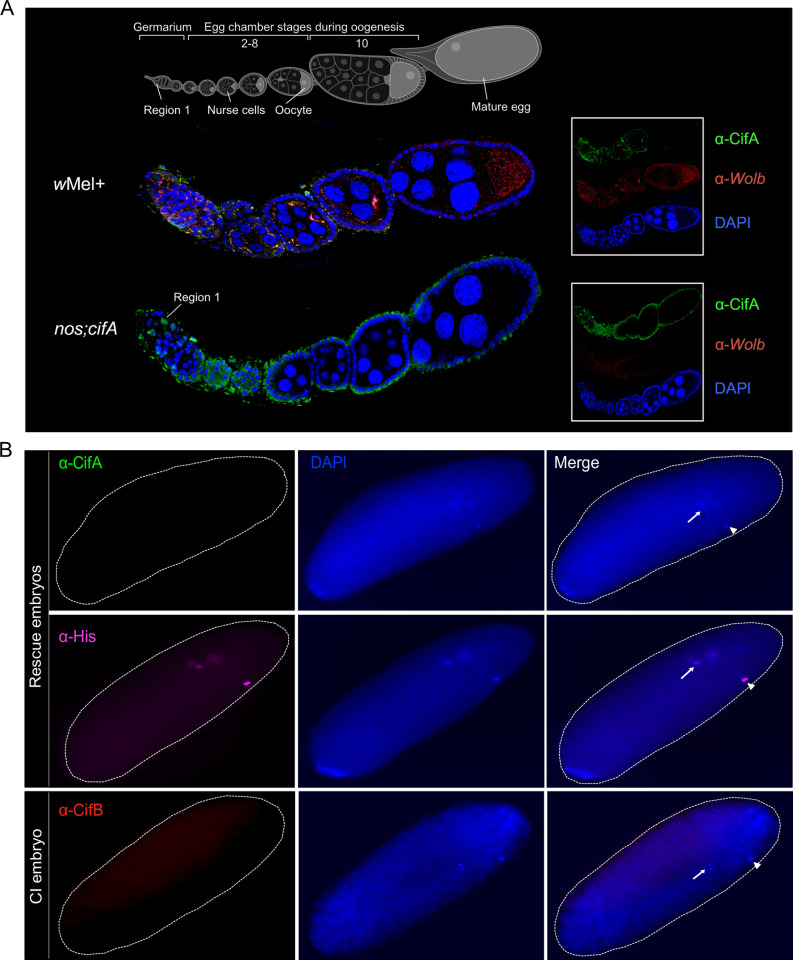
Fig 6. CifA is present in early oogenesis and absent in late-stage egg chambers.
Both CifA and CifB are absent in CI and rescue embryos. (A) Schematic representation of Drosophila melanogaster ovariole at the top illustrates the stages of oogenesis from left to right. Image was created with BioRender.com. Immunostaining assay indicates localization of CifA (green) to the cyst DNA (blue labeled with DAPI) in region 1 of the germarium of Wolbachia-uninfected transgenic cifA line. In wMel+ line, CifA colocalizes with Wolbachia (red) in the germarium, nurse cells and oocyte cytoplasm along 2–8 stages of egg chambers. CifA is absent in stage 10 egg chamber, whereas Wolbachia signals persist. In the transgenic cifA line, we note the observed autofluorescence in green channel outlining the tissue morphology does not signify CifA signals. Ovariole images were manually adjusted in Affinity designer software to align egg chamber stages in the same plane. (B) Immunofluorescence of CifA (green) and CifB (red) in approximately 30- to 60-minute-old embryos obtained from rescue (cifAB male × wMel+ female) and CI crosses (nos;cifAB male × wMel− female). Histone antibody labeling core-histones (magenta) was used as a positive control. Histone signals were detected colocalizing with host DNA, labeled with DAPI (blue), whereas no CifA and CifB signals were detected. Dotted white embryonic periphery is drawn around the embryo shape. White arrows indicate dividing nuclei post fertilization and arrowheads indicate polar bodies. CI, cytoplasmic incompatibility.