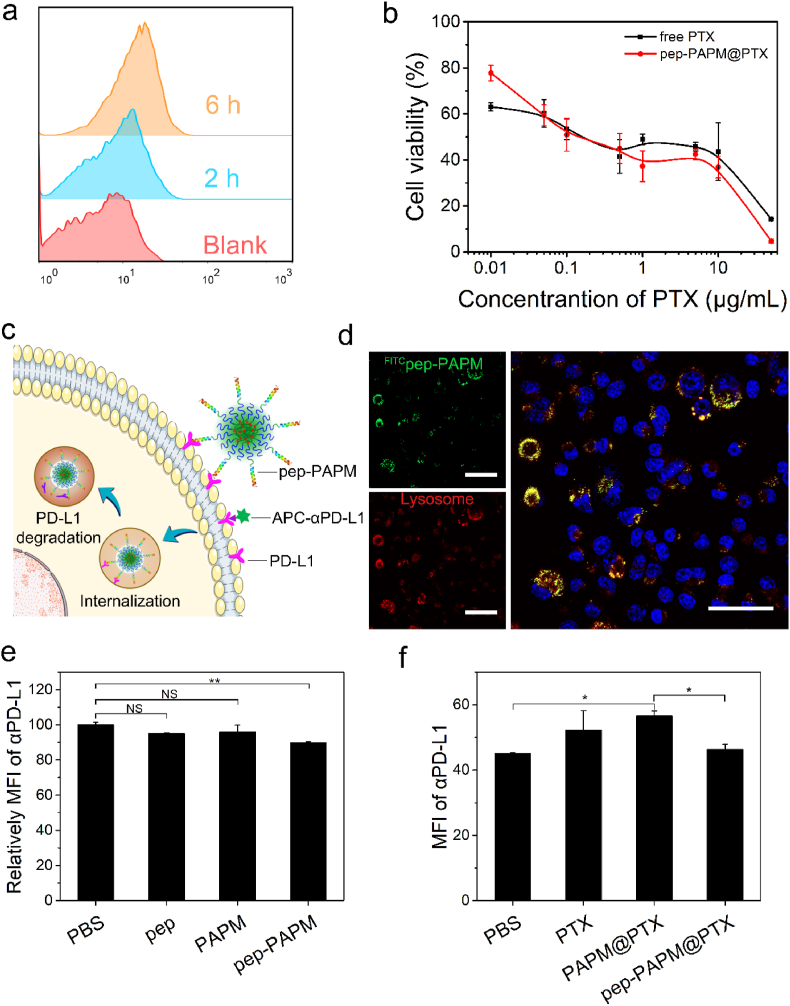
Fig. 2.
Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of pep-PAPM@PTX and its possible mechanism of downregulating PD-L1 expression. (a) Time-dependent cellular uptake of pep-FITCPAPM by 4T1 cells measured by flow cytometry. (b) Cytotoxicity assays of PTX and pep-PAPM@PTX against 4T1 cells after 48 h treatment. (c) Schematic illustration of the multivalent binding of pep-PAPM towards PD-L1 to drive PD-L1 into lysosome degradation. (d) Colocalization of pep-FITCPAPM and lysosome after 4 h incubation with 4T1 cells. Nuclei stained with Hoechst 33,342 are shown in blue, lysosomes stained with LysoTracker Red are shown in red, and pep-FITCPAPM is shown in green. Scale bar: 50 μm. (e) The flow cytometric analysis of the cell surface PD-L1 in 4T1 cells treated by different groups for 1 h at 4 °C (pep eq. dose of 100 μg/mL). (f) The flow cytometric analysis of the cell surface PD-L1 in 4T1 cells treated by different groups for 24 h at 37 °C (PTX eq. dose of 20 μg/mL).