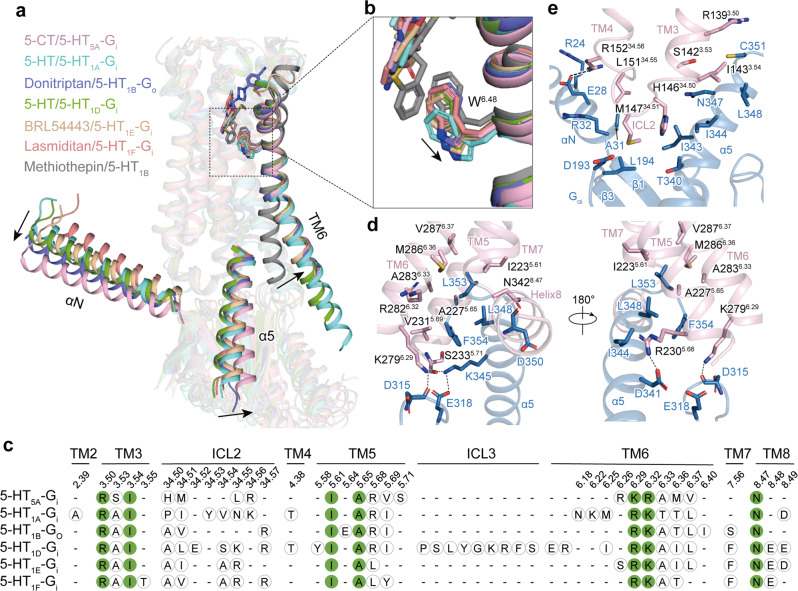
Fig. 4. Structural features of the activation and Gi/o coupling of 5-HT5A and other Gi/o-coupled 5-HT receptors.
a The activation of 5-HT5A and other Gi/o-coupled 5-HT receptors. The outward movement of TM6 of agonist-bound Gi/o-coupled 5-HT receptors compared with methiothepin-bound 5-HT1B in the inactive state is shown as a black arrow. The movements of the αN and α5 helix of Gαi protein in the 5-HT5A–Gi complex relative to that in other Gi/o-coupled 5-HT receptors are indicated as black arrows. The structures of the active 5-HT5A (light pink), 5-HT1A (cyan, PDB: 7E2Y), 5-HT1B (purple, PDB: 6G79), 5-HT1D (green, PDB: 7E32), 5-HT1E (wheat, PDB: 7E33), 5-HT1F (coral, PBD: 7EXD) and inactive-state 5-HT1B (gray, PDB: 4IAQ) complexes were superimposed based on TM2, TM3 and TM4. b Structural comparison of ligands and the W6.48 residues of active 5-HT receptors with that of inactive 5-HT1B. Ligands directly contact W6.48. Compared with methiothepin, the inverse agonist of 5-HT1B, agonists trigger the rotameric switch of W6.48, which leads to the outward movement of TM6. c The sequence alignment of receptor residues at receptor–Gi/o protein interfaces. The conserved residues are highlighted in solid green circles. d, e Detailed interactions between 5-HT5A and the Gαi subunit. Detailed Interactions between TM5, TM6, and the TM7–helix 8 junction of 5-HT5A and the α5 helix of the Gαi subunit (d). Detailed interactions between ICL2 of 5-HT5A and the α5 and αN helices, β1 and β3 strands of the Gαi subunit (e).