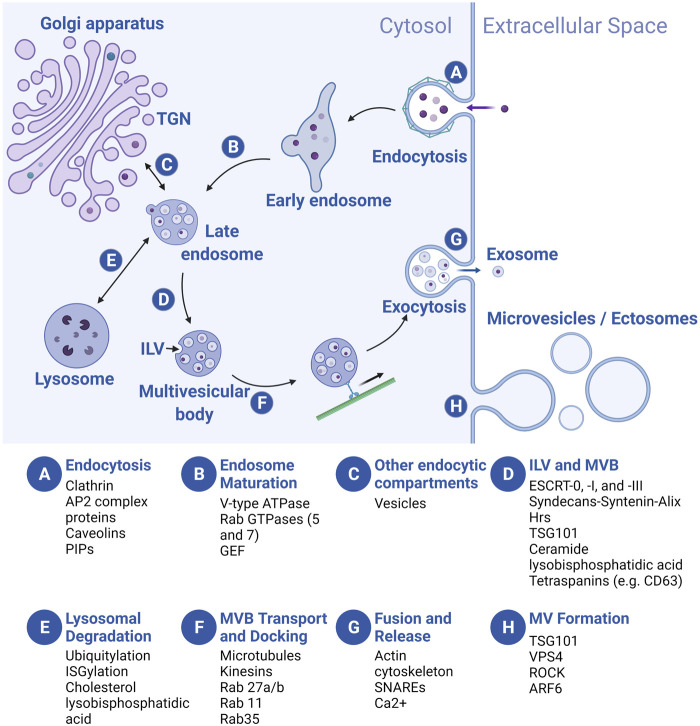
FIGURE 3.
Overview of EV biogenesis. Letters in blue circles indicate steps in EV biogenesis. Regulators of each step are listed below. Exosome biogenesis begins with an endocytic event (A) that results in the formation of an early endosome (EE) which then matures into a late endosome (LE) (B). During maturation, LEs receive cargo from several endocytic compartments such as the Golgi apparatus (C), and cargo-filled vesicles bud internally (intraluminal vesicles, ILVs), creating the multivesicular body (MVB) (D). MVBs are sorted to the lysosome for degradation (E), or they traffic towards the plasma membrane (PM) (F) where they fuse and release the ILVs, now called exosomes (G). Microvesicles (MVs) bud off directly from the PM (H). For simplicity, we depict MVB formation following late endosome maturation but the MVB can de-attach from vesicular regions of both the early and late endosomes and ILVs can be added at multiple points along the pathway. TGN, trans-Golgi network. Created with BioRender.com.