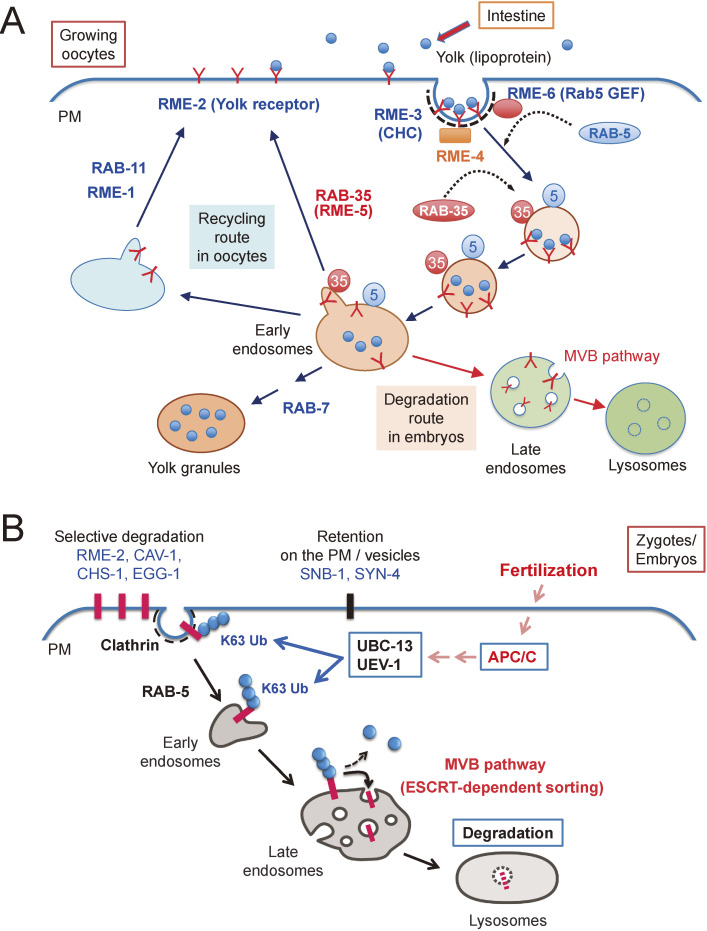
Figure 2.
(A) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of yolk components. Yolk components secreted from the intestine are endocytosed by the growing oocytes. RME-2 is a yolk receptor that is recycled between the plasma membrane and endosomes to deliver yolk components to yolk granules in growing oocytes. Many proteins, including RME proteins are involved in this process. After fertilization, RME-2 is delivered to lysosomes via the multivesicular body (MVB) pathway for degradation. CHC, clathrin heavy chain; PM, plasma membrane. (B) Selective degradation of maternal membrane proteins in embryos. Some of the maternal membrane proteins (RME-2, CAV-1, CHS-1, and EGG-1) are internalized by clathrin-dependent endocytosis and delivered to lysosomes via the MVB pathway. This process depends on meiotic cell cycle progression triggered by anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C). Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2) such as UBC-13 and its variants, UEV-1, are involved in the ubiquitination of maternal membrane proteins. By contrast, SNB-1 and SYN-4, which are general factors regulating membrane trafficking, remain after fertilization and continue to function in embryos. PM, plasma membrane.