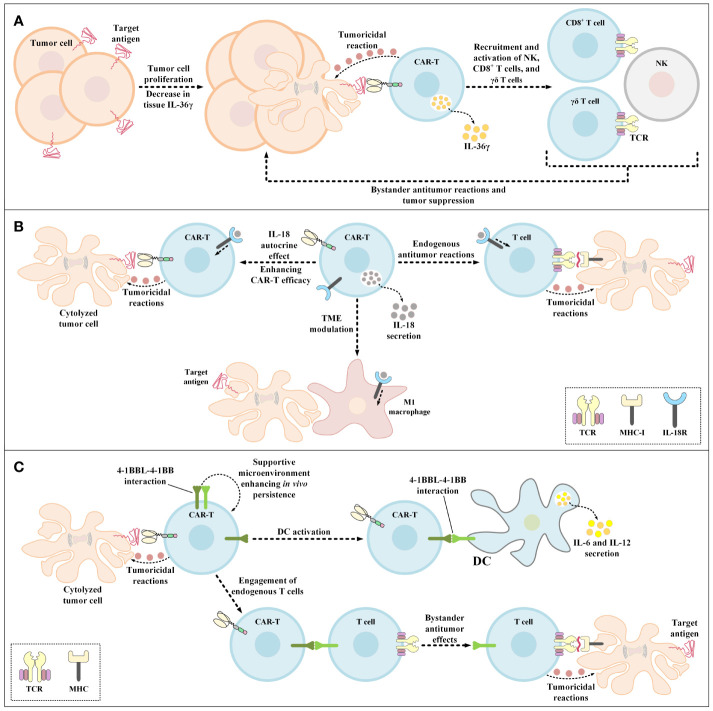
Figure 5.
Bystander antitumor effect induction using IL-36γ-secreting CAR-Ts, IL-18-secreting CAR-Ts, and 4-1BBL-expressing CAR-Ts. (A) The effects of IL-36γ secreted by IL-36γ-secreting CAR-Ts. IL-36γ secreted by these engineered CAR-Ts results in the recruitment and activation of endogenous immune effector cells, which include type 1 lymphocytes such as CD8+ T cells, NK cells, and γδ T cells. These endogenous immune effector cells can mediate bystander antitumor immune reactions resulting in the suppression of tumor cell proliferation. (B) The effects of IL-18 secreted by IL-18-secreting CAR-Ts. CAR-T-secreted IL-18 has autocrine effects on the CAR-Ts themselves enhancing the antitumor activity of these cells. In case of endogenous tumoricidal effects, CAR-T-secreted IL-18 recruits endogenous T cells to the tumor sites and triggers their bystander antitumor reactions. Moreover, CAR-T-secreted IL-18 also modulates the TME and recruits M1 macrophages to the tumor site which results in M1 macrophage-mediated tumor cell cytolysis. (C) The beneficial effects of 4-1BBL expression by CAR-Ts. 4-1BBL-expressing CAR-Ts demonstrate enhanced functionality in comparison with their conventional counterparts in three ways. The 4-1BBL expressed on CAR-Ts self-interacts with the 4-1BB on these cells resulting in their enhanced in vivo persistence. 4-1BBL expressed on CAR-Ts also interacts with 4-1BB on the surface of DCs, inducing DC-secretion of IL-6 and IL-12. Additionally, CAR-T-expressed 4-1BBL interacts with 4-1BB on the surface of endogenous T cells leading to MHC-mediated bystander tumoricidal reactions. 4-1BBL, 4-1BB ligand; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; DC, dendritic cell; IL-18R, IL-18 receptor; MHC-I, major histocompatibility complex class I; NK, natural killer cells; TCR, T-cell receptor; TME, tumor microenvironment.