Figure 5.
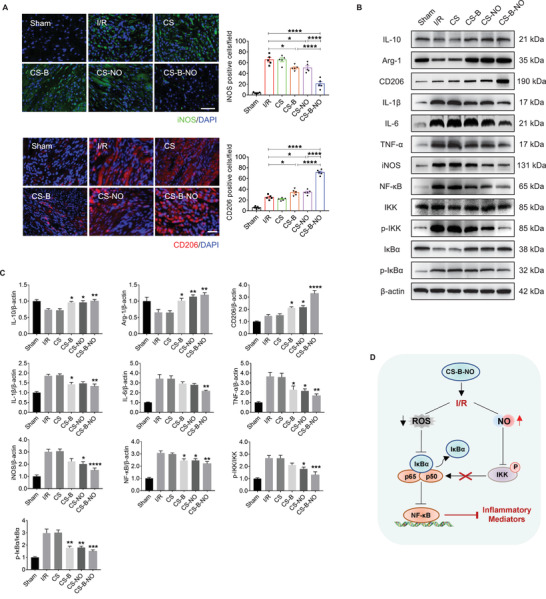
CS‐B‐NO hydrogel inhibited NF‐κB inflammatory signaling pathway by regulating local ROS/NO balance after myocardial I/R injury. A) Macrophage polarization was detected by immunofluorescence staining targeting iNOS and CD206, the markers of M1 and M2 macrophage phenotype, respectively (scale bar = 50 µm). B,C) Representative Western blot images and quantitative data showing the expression of IL‐10, Arg‐1, CD206, IL‐1β, IL‐6, TNF‐α, iNOS, NF‐κB, IKK, p‐IKK, IκBα, and p‐IκBα, in the hearts after I/R injury with different treatments. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 5 animals for each group, Significant differences were detected by one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons tests, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001. D) Schematic illustration summarizing the mechanism of CS‐B‐NO hydrogel on inhibiting the NF‐κB signaling pathway after I/R injury.
