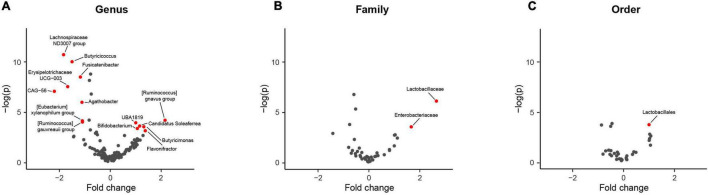
FIGURE 3.
Comparison of taxa abundance between household (HC) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients at different phylogenetic levels reveals specific differences. Volcano plots representing abundance differences (fold change) of different taxa between HC and PD patients showed statistically significant [-log (p) > 3; fold change > ± 1.2] compositional differences at the genus, family and order levels (represented by red dots), indicative of a PD-related GM composition. With regards to PD patients, there was statistically significant overrepresentation of Bifidobacterium, Candidatus Soleaferre, Butyricimonas, Flavonifractor, [Ruminococcus] gnavus group, and Faecalibacterium sp. UBA1819 and underrepresentation of Butyricicoccus, Fusicatenibacter, Lachnospiraceae ND3007 group, Erysipelotrichaceae UCG-003, Agathobacter, [Eubacterium] xylanophilum group, [Ruminococcus] gauvreauii group, and Firmacutes bacterium CAG:56 at the genus level (A), overrepresentation of Lactobacillaceae and Enterobacteriaceae at the family level (B) and overrepresentation of Lactobacillales at the order level (C). The largest fold change was observed for increased Lactobacillaceae taxa abundance (2.7 fold increase).