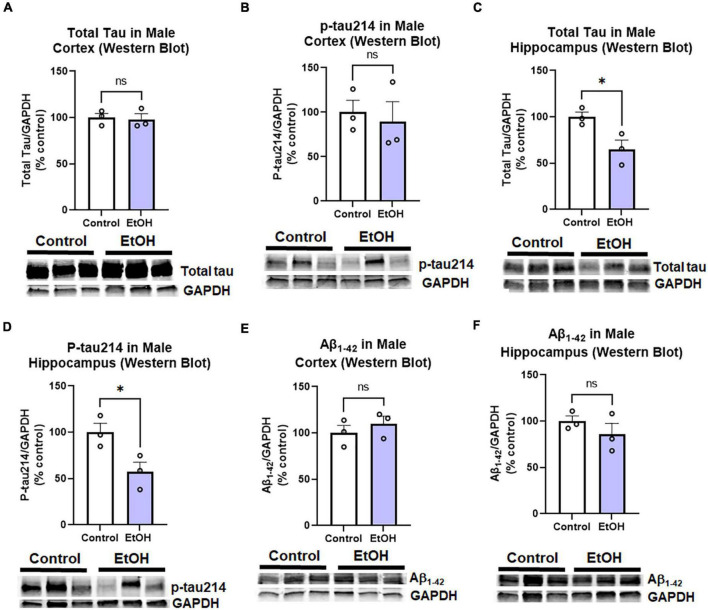
FIGURE 4.
Persistent effects of ethanol on tau and Aβ proteins in male 3xTg-AD mice. Adult male 3xTg-AD mice received EtOH (5g/kg/d, i.g., 5d on 2d off, N = 3) or the same schedule of water (i.g., N = 3) for 3 months (P168–P264), followed by prolonged abstinence with assessment at 14 months. Pathologic tau and Aβ protein levels were measured in cortex and hippocampus by western blot. (A,B) Tau species in cortex. EtOH had no persistent effects on neither (A) total tau, p = 0.8 nor (B) phosphorylated tau214 (p-tau214) p = 0.7. (C,D) Tau in hippocampus. In the hippocampus, EtOH caused a persistent reduction in (C) total Tau, 35% reduction, *p < 0.05, and (D) p-tau214, 43% reduction, *p < 0.05. (E,F) Aβ1–42 levels. EtOH had no persistent impact on levels of Aβ1–42 in either male (E) cortex, p = 0.4 or (F) hippocampus, p = 0.3. *p < 0.05, t-test.