FIGURE 7.
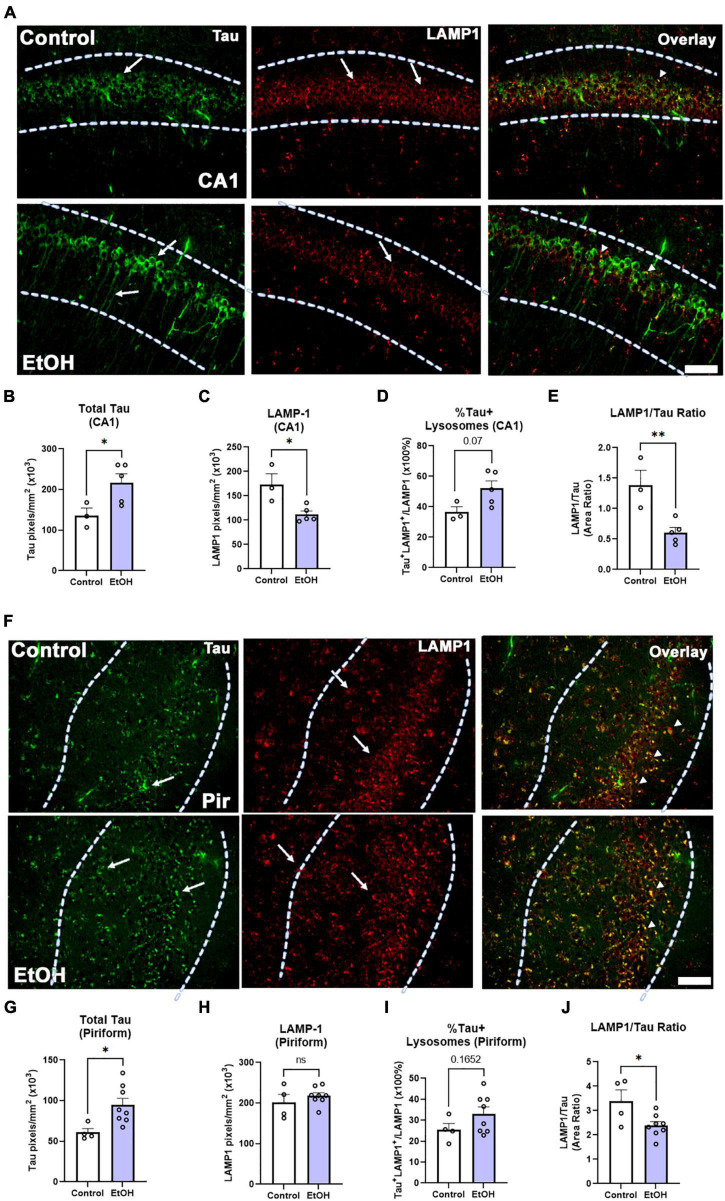
Chronic binge ethanol causes persistent increase in tau and loss of LAMP1 positive lysosomes in hippocampus of female 3xTg-AD mice. Adult female 3xTg-AD mice received EtOH (5g/kg/d, i.g., 5d on 2d off) for 3 months (P168–P264), followed by prolonged abstinence until 14 months. (A) Total tau and lysosomal LAMP1 involved in autophagy and tau clearance were measured by co-immunofluorescence (co-IF). Left-pointing arrows denote tau stain in cell body and processes. Right pointing arrows denote punctate LAMP-1 staining. Arrowheads denote co-localization. (B) Quantification of total tau in the CA1 region revealed a persistent increase by 60%, *p < 0.05, t-test and (C) quantification of lysosomal LAMP1 in the CA1 region indicated a persistent reduction by 35%, *p < 0.05. (D) Overlaying total tau and LAMP1 revealed a trend toward a 43% increase in the percent of tau-positive lysosomes in the CA1, p = 0.07, however, (E) there was also a sharp 59% decline in the amount of LAMP1 overlapping with total tau in the CA1, **p < 0.01. (F) Total tau and lysosomal LAMP1 involved in autophagy and tau clearance were measured by co-IF in piriform cortex (Pir). Left-pointing arrows denote tau stain in cell body and processes. Right pointing arrows denote punctate LAMP-1 staining. Arrowheads denote co-localization. (G) Ethanol caused a persistent increase in tau in the piriform cortex (Pir), 56%m*p < 0.05, t-test. (H) Ethanol had no effect on LAMP1 level in Pir. (I) Ethanol caused a trend toward an increase in the percent of Tau+ lysosomes p = 0.17. (J) Ethanol caused a persistent reduction in the ratio of LAMP1 to Tau. *p < 0.05, t-test. Scale bar = 50μm.