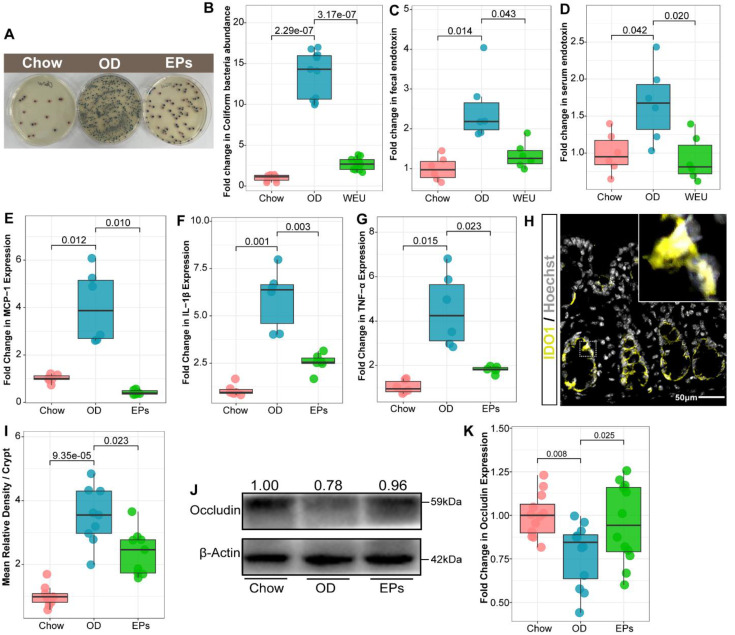
Figure 3.
EPs inhibited the expansion of E. coli in the gut and alleviated the subsequent experimental colitis. (A-B) Chromogenic culture for assessing the abundance of E. coli in colonic contents. Supplementation with EPs inhibited the OD-induced expansion of E. coli in the colon (n = 11 for each group). OD increased the endotoxin concentration in colon contents (C) and serum (D), rescued by supplementation with EPs (n = 6 individuals/group). Relative mRNA expression levels of MCP-1 (E), IL-1β (F), and TNF-α (G) in colonic tissues was assessed using qRT-PCR (n = 6 individuals/group). (H) Fluorescent immunostaining of IDO1 (yellow) in mouse colonic sections. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst (white). (I) The expression of IDO1 was significantly enhanced in OD, which was inhibited by supplementation of EPs (n = 9 slices from 3 mice). (J-K) Immunoblot analysis for occludin in colon tissue. Quantification: band intensity normalized to β-actin (n = 12 for each group). Statistical significance compared to OD by one-way ANOVA, adjusted for multiple comparisons by Dunnett post-hoc. Lines in boxes represent median, top and bottom of boxes represent first and third quartiles, and whiskers represent 1.5 interquartile range.