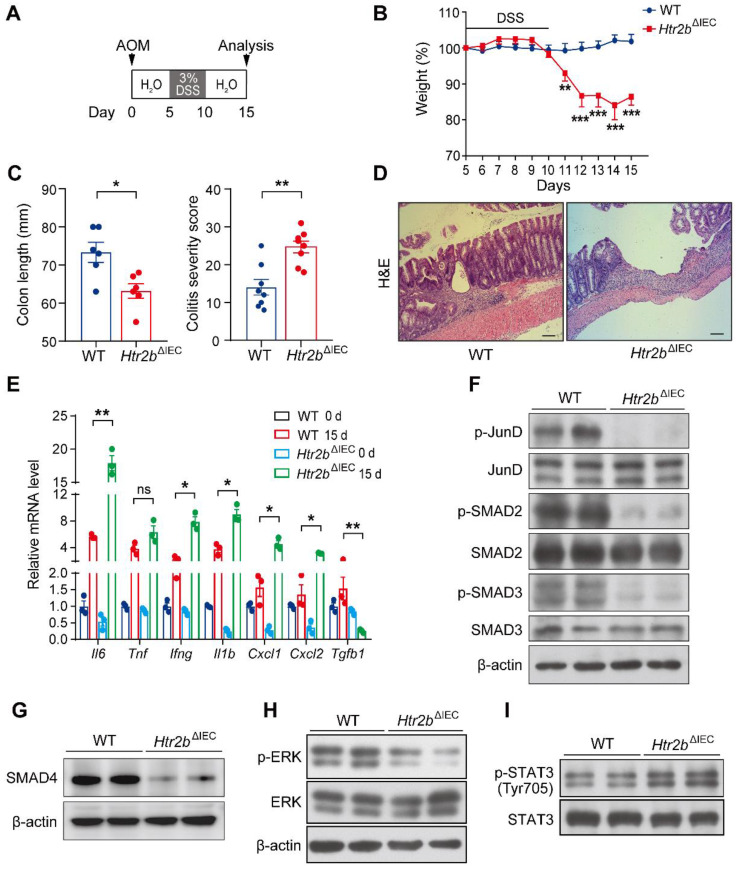
Figure 2.
Deletion of 5-HT2B inhibits the TGF-β signaling pathway and enhances the inflammatory response. (A) Schematic overview of the AOM/DSS model of acute colitis in mice. (B) Body weight of WT (n = 8) and Htr2bΔIEC (n = 8) mice during AOM/DSS treatment. (C) The colon length and colitis severity score of WT and Htr2bΔIEC mice (n = 6-8) with acute colitis. (D) H&E staining of colon sections from WT and Htr2bΔIEC mice with acute colitis on day 15. (E) Proinflammatory cytokine mRNA levels (n = 3) in whole colonic mucosa specimens from WT and Htr2bΔIEC mice. (F) Levels of total protein and phosphorylated JunD, SMAD2, and SMAD3 in the colonic epithelium of WT and Htr2bΔIEC mice. (G) SMAD4 protein levels in the colonic epithelium of WT and Htr2bΔIEC mice. (H) Levels of total protein and phosphorylated ERK in the colonic epithelium of WT and Htr2bΔIEC mice. (I) Levels of total protein and phosphorylated STAT3 in the colonic epithelium of WT and Htr2bΔIEC mice. Scale bars, 100 μm. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM. ns: not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; Two-way ANOVA (B), unpaired Student's t-test (C) and One-way ANOVA (E).