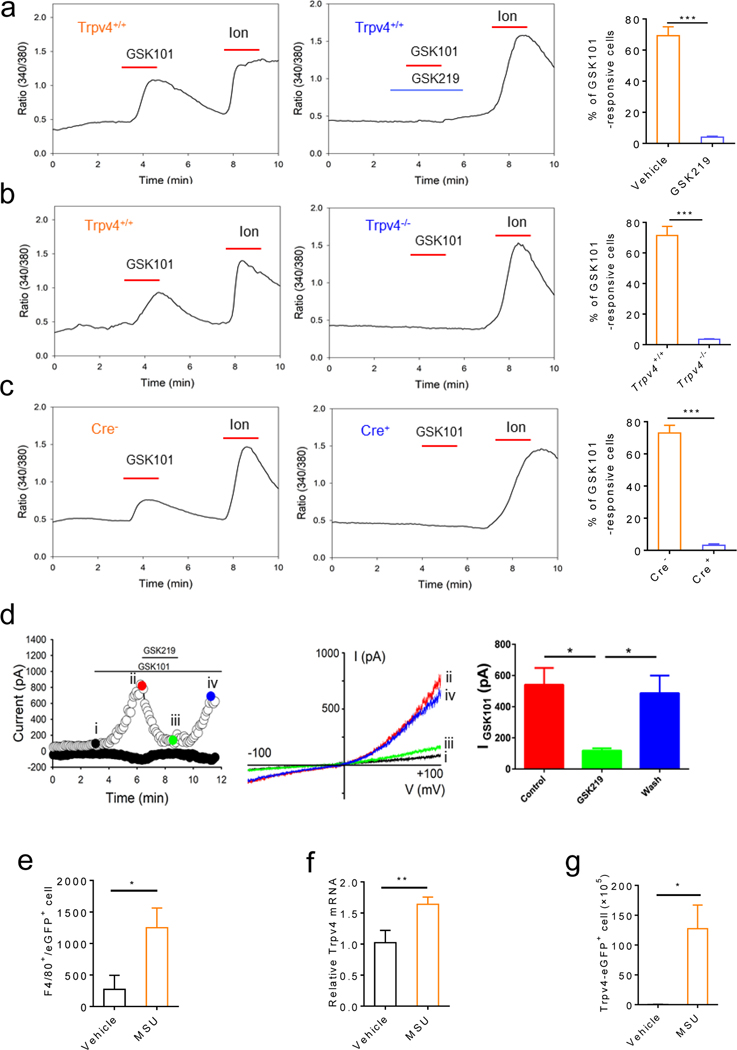
Figure 2: TRPV4 is functionally expressed by the synovial MΦ and TRPV4 expression and the number of TRPV4+ MΦs are increased by MSU crystals.
(a) Representative traces showing GSK101 (0.3 μM)-elicited [Ca2+]i response in freshly dissociated synovial MΦ single-cell suspensions from the Trpv4+/+ mice. Pre- and co-applied GSK219 (1 μM) abolished the GSK101 action. Summarized data on the right show the reduction of the percentage of GSK101-responsive synovial MΦs by GSK219. (b) Representative traces showing that GSK101 induced a [Ca2+]i response in the synovial MΦ single-cell suspensions from the Trpv4+/+ but not Trpv4−/− mice. Summarized data on the right show that genetic ablation of TRPV4 function reduces the percentage of GSK101-responsive synovial MΦs. (c) Representative traces showing the GSK101-induced [Ca2+]i response in the synovial MΦ single-cell suspensions from the Cre- but not Cre+ Cx3cr1CreERT; Trpv4f/f mice. Summarized data on the right show reduced the percentage of GSK101-responsive synovial MΦs isolated from the MΦ-specific TRPV4 cKOs. (d) Left: Representative time course of membrane currents evoked by GSK101 (0.3 μM) at +100 mV and −100 mV membrane potentials with and without co-applied GSK219 (1 μM). Horizontal bars denote the time courses for applications of GSK101 and GSK219. Middle: Representative current-voltage curves taken at time points i, ii, iii, and iv (color-coded) from the time course on the left. A ramp protocol elicited by a voltage ramp from −100 mV to +100 mV was used. Quantification of the effect of GSK219 on GSK101-activated whole-cell membrane current recorded at +100 mV is shown on the right. (e) Flow cytometry shows that the number of TRPV4-eGFP+ cells increased significantly 6 hr after IA injections of MSU crystals (0.8 mg/site). (f) TRPV4 mRNA expression in the synovial lining of the Trpv4eGFP mice treated with vehicle or MSU crystals. (g) Quantification of the number of the F4/80+/eGFP+ synovial MΦs in response to treatment with MSU crystals or vehicle. Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t test (a-g), *P<.05, **P<.01, ***P<.001. n=5–6 per group.